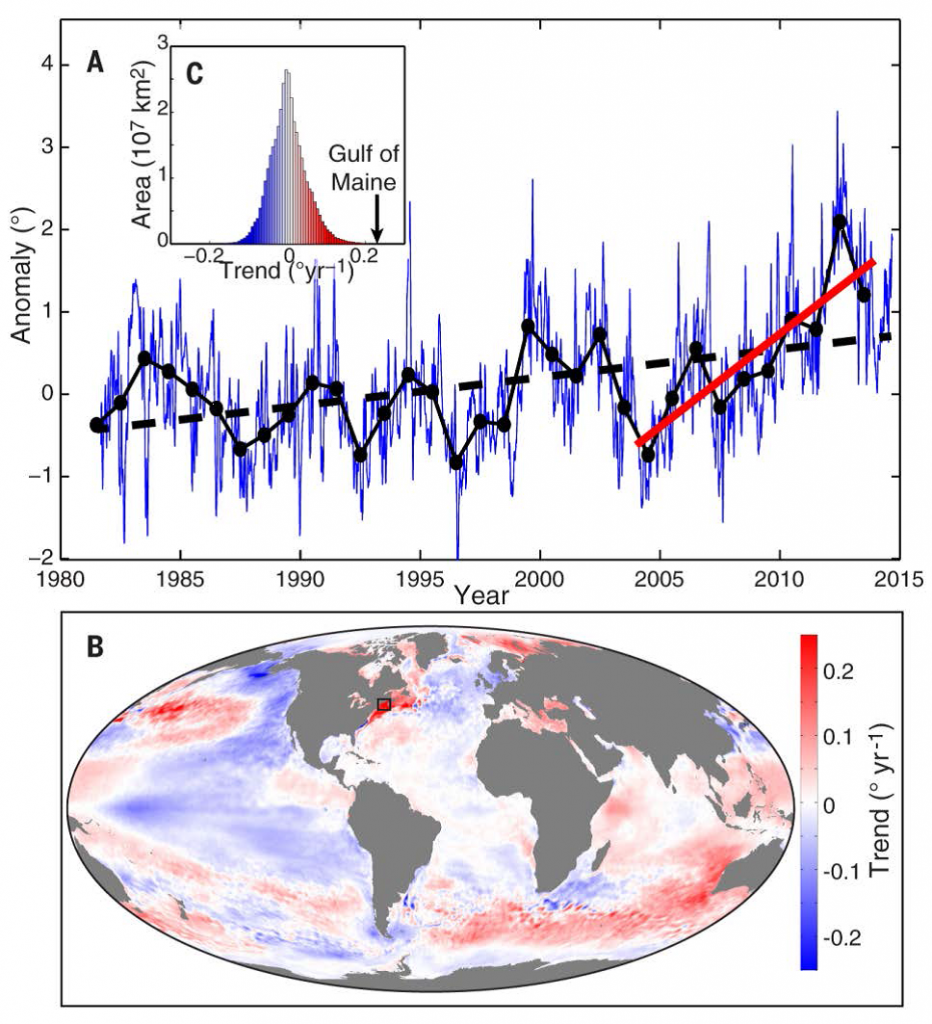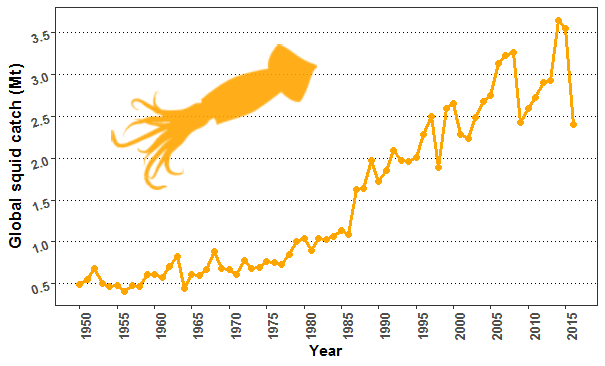
Global reported squid catches (Millions of metric tons, 1950-2015). While squid catches have increased in recent years, year to year changes have also increased. Data accessed from FAO database. Plot by R. Boenish
Besides being the star in calamari appetizers, squid play the crucial roles of both predator and prey in marine ecosystems. Globally, squid can be found in nearly every ocean habitat from seagrass beds, to coral reefs, to the open ocean. Squid fisheries provide livelihoods and high-quality protein to communities, large and small all over the world. And as it turns out, studying squid can teach us valuable lessons about how to build climate-resilient fisheries. A new paper in Fisheries Research will help fishery managers predict where jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) populations might migrate under different scenarios of climate change, and help researchers understand why some species are more resilient than others.
While overall squid catches (all species combined) have increased in recent years, it is unclear what the future will hold in the face of climate change and other pressures. Healthy ecosystems depend on resilience from all links of the food chain. This research, which I contributed to along with a number of leading marine research organizations including Shanghai Ocean University, The University of Washington and The University of Maine, suggests that squid may play a more important role in improving climate resilience in the world’s fisheries than previously thought. Read More