The American Natural Gas Association (ANGA) released a paper in March titled “Texas Natural Gas: Fuel for Growth,” to a lot of press, and rightly so. The paper correctly cites several benefits of using and producing natural gas in Texas: it is produced in-state, has water use and air-quality benefits when compared to coal and helps to fund state and local governments through taxes.
Unfortunately, the paper also makes some claims that are difficult to take seriously; perhaps the first warning sign should be that while the paper was presented as an economic analysis, the authors have no economic credentials. Dr. Michael J. Economides, a chemical and biomolecular professor at the University of Houston, and petroleum engineering consultant Philip E. Lewis spend little time worrying about the details in this report, serving up a heaping helping of “number salad.”
For instance, the $7.7 billion “loss” is calculated by projecting the potential use of gas in Texas, if it had followed the national trend, against the actual use. But in looking at the data, it’s not clear that the Texas fuel mix ever tracked the national fuel mix. Even more importantly, looking at the authors’ own slides, Texas uses 20% more natural gas in its fuel mix than the nation. If anything, the national fuel mix is following the trend set long ago by Texas —adding more natural gas and wind, while decreasing coal output.
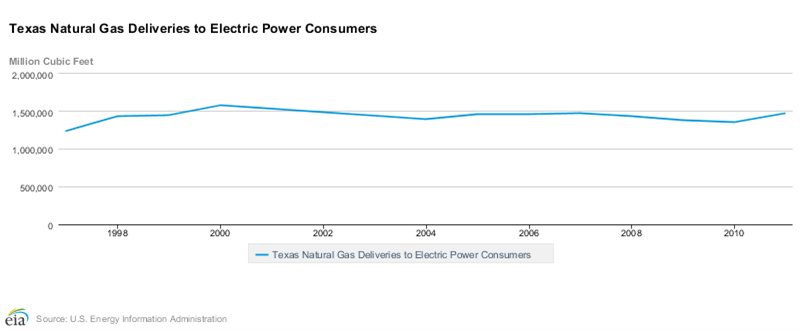
What might shock the authors is that natural gas consumption in the electric power sector has increased by around 5,000 one thousand cubic feet of gas (MCF) since 2006, 800 MCF in transportation and nearly 10,000 MCF in the industrial sector.
There are so many misleading statistics and inaccuracies that we could practically write a report on the report, but instead I’ll just focus on one aspect that stands out in particular.
When it comes to comparing natural gas to coal power, the authors are quick to cite the many local benefits of using natural gas energy produced in Texas: it’s cleaner than coal and creates local jobs and a local tax base. Wind energy has largely produced the same benefits: local wind power has brought jobs and a growing tax base and population to rural Texas counties that “had seen consistent, significant population losses since 1950.” On top of the economic development benefits, where natural gas beats coal in reducing pollution, wind energy beats both by reducing pollution basically to zero. But when it comes to discussing any of these benefits from wind energy in the report, the silence is deafening.
Natural gas is reshaping our energy landscape. And, done right—with the proper, mandatory environmental safeguards in place and reduced methane leakage rates—compared to coal plants, natural gas power plants offer other distinct air quality benefits. It emits less greenhouse gases than coal when combusted and avoids mercury and other dangerous air pollutants that come from coal.
However, the same – and more – can be said about wind energy and Texas’ potential clean energy resources, including solar and geothermal power, among others. Rather than pitting our local clean energy resources against each other as this report does, we should seek to expand and diversify our clean energy mix, reaping health, environmental, economic and security benefits.