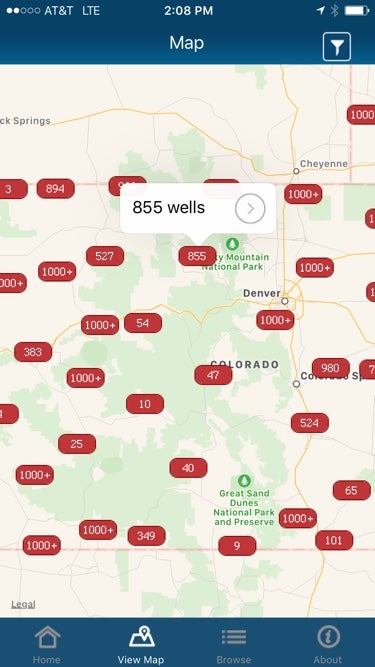
 Across the U.S. more than 15 million people live within a mile of an oil or gas well – and a new app is making it easier for those people to know exactly where those wells are located within their neighborhoods.
Across the U.S. more than 15 million people live within a mile of an oil or gas well – and a new app is making it easier for those people to know exactly where those wells are located within their neighborhoods.
The WellFinder app uses data from state agencies to help users know not only the exact location of these wells, but also how old they are, who operates them, whether they are still active, what type of well it is (i.e. oil, gas, injection) and who to call if something doesn’t appear to be functioning properly.
Companies and regulators often find out about water contamination and air pollution from the people who live near these facilities. With this kind of transparent data now at our fingertips, communities can keep a more watchful eye on oil and gas operations – ultimately enhancing the environmental performance of the industry. Read More










 By: Jori Mendel, AT&T Smart Cities, and Chandana Vangapalli, former Environmental Defense Fund Climate Corps Fellow
By: Jori Mendel, AT&T Smart Cities, and Chandana Vangapalli, former Environmental Defense Fund Climate Corps Fellow The U.S. electric grid is old and frayed, yet innovative technologies – modern sensors, smart meters, and advanced telecommunications – offer hope to update it to become more modern, efficient, and clean. What all these smart-grid tools have in common is data. How we utilize the enormous quantities of information about how we move and use electricity will have major impacts on markets, customers, the environment, and our future electricity system.
The U.S. electric grid is old and frayed, yet innovative technologies – modern sensors, smart meters, and advanced telecommunications – offer hope to update it to become more modern, efficient, and clean. What all these smart-grid tools have in common is data. How we utilize the enormous quantities of information about how we move and use electricity will have major impacts on markets, customers, the environment, and our future electricity system. The need to plan for and design a more efficient, cleaner, and resilient electricity
The need to plan for and design a more efficient, cleaner, and resilient electricity 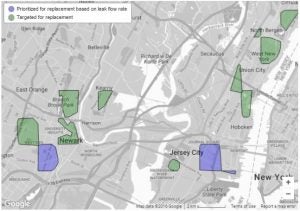
 On any given day, half a million Americans
On any given day, half a million Americans