Investors managing oil and gas portfolios are contending with major disruption as two interrelated crises play out: the global COVID-19 pandemic and extreme volatility in the price of oil. Yet even before these events, cracks were showing in the sector’s financial footing. Pressure has been rising on industry to improve returns, while demand to deliver on Environmental Societal Governance initiatives has never been higher.
Into this mix comes new data from scientists working with EDF’s PermianMAP initiative showing that methane emissions in the Permian Basin, the world’s largest oil field, is nearly three times the rate reported in Environmental Protection Agency’s nationwide statistics.
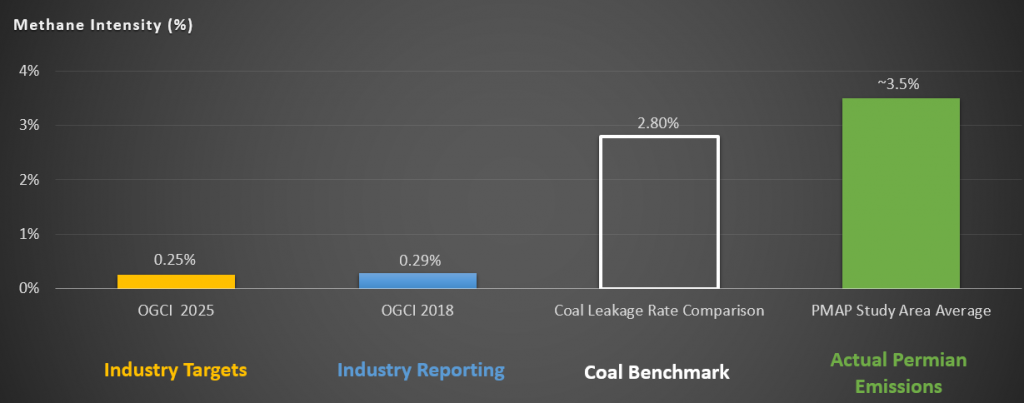
The 3.5% loss rate estimated in the data area is roughly 15 times higher than reduction targets set by leading producers, and significantly higher than many companies have reported. It translates to 1.4 million tons of wasted gas each year, enough to meet the annual natural gas needs of every home in Dallas and Houston combined.
The findings surface a material risk to oil and gas investors and to the future of natural gas from the Permian Basin. At current emissions rates from the basin, burning Permian natural gas for electricity does more near-term climate damage than coal.
A year from now, the U.S. oil and gas sector may look very different for many of the independent operators who make up a large portion of Permian producers. Withstanding this period of economic turbulence will require companies to make tough decisions. Yet even in this time of crisis, operators must keep an eye on future market demands, operational excellence and climate performance.
Permian study findings
The Permian sprawls across West Texas and New Mexico and has more than 100,000 operating well sites. Between October 2019 and March 2020, EDF scientists collaborated with academic institutions to collect data using tower-based monitors, ground-based mobile sensors, helicopters and fixed wing aircraft across a 10,000-square-kilometer study area responsible for 40% of Permian production.
The estimated 3.5% leak rate reflected in the new data stands in stark contrast to the .20% leakage rate agreed to by the 13 of the world’s largest operators in the Oil and Gas Climate Initiative, representing 30% of global oil and gas production. Furthermore, the emissions rate seen in the Permian is more than 10 times the methane intensity of 0.29% that OGCI has been reporting for 2018.