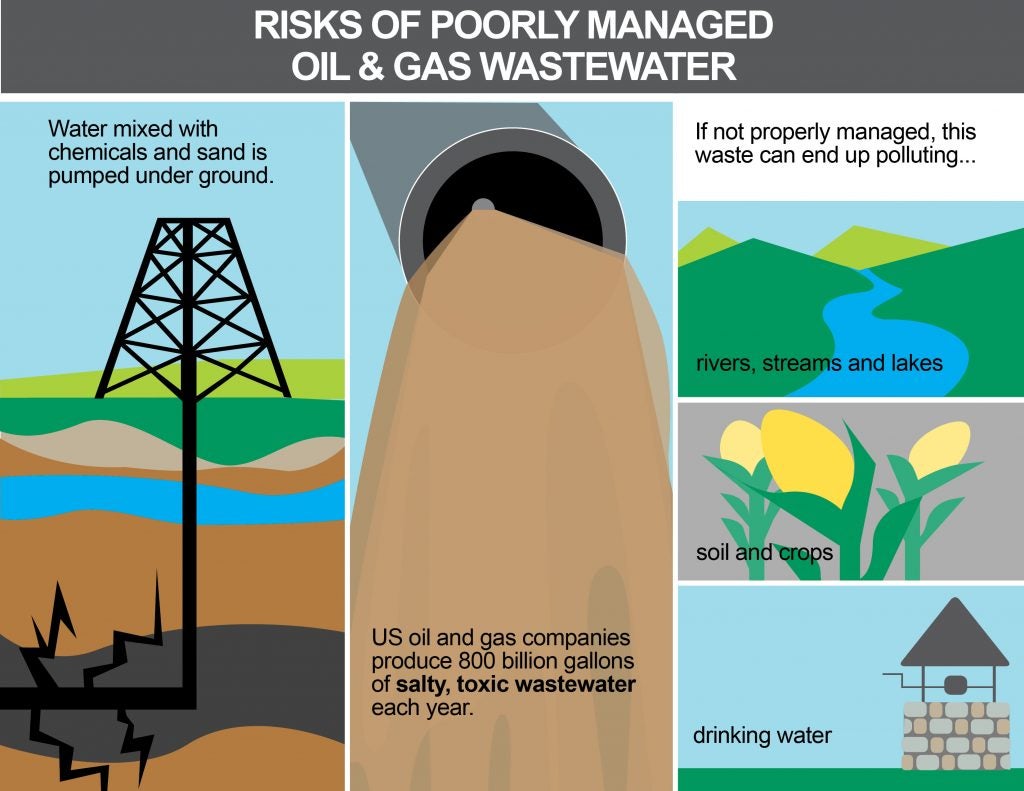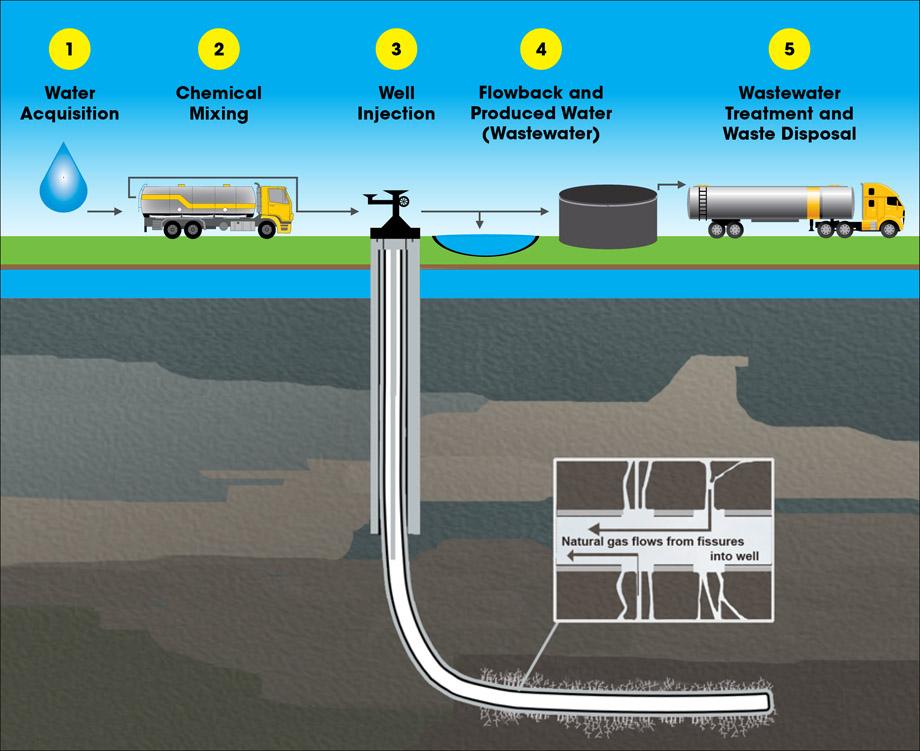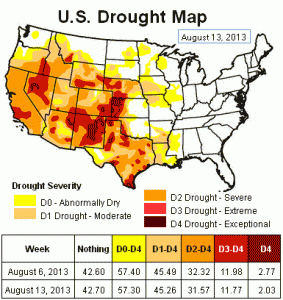
Source: feww.wordpress.com
Over the past few weeks, I’ve written a number of posts to help shed light on the fundamental connection between energy and water. Because many of our energy sources gulp down huge volumes of water, it’s imperative that we break down the long-standing division between energy and water planning — especially in drought-prone states like Texas. I’d like to take a step back and look at how Texas’ neighbors are addressing energy and water co-management. While Texas may be an extreme example, looking toward its immediate neighbors could provide ideas and best practices to improve the state’s situation.
A number of western states are facing many of the same challenges as Texas. Electricity production is a major drain on the region’s water supply. A study co-authored by Western Resource Advocates and EDF showed that thermoelectric power plants, such as coal, natural gas and nuclear, in Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico, Nevada and Utah consumed an estimated 292 million gallons of water each day in 2005 — roughly equal to the amount of water consumed by Denver, Phoenix and Albuquerque combined (and we’re talking water consumption, not just withdrawals). Like Texas, the western states face a future of prolonged drought. Scientific models predict climate change will increase drought throughout the Southwest, placing greater stress on the region’s delicate water supply.
Additionally, electricity production, numerous thirsty cities and widespread agricultural activity all strain the water system, too. Because so many flock to western states for fishing, kayaking, rafting and other recreational water activities, setting the region’s water system on a sustainable path is a critical economic issue. The exceptional challenges facing western states have already prompted some states to consider the energy-water nexus when planning to meet future water and electricity needs. Read More »