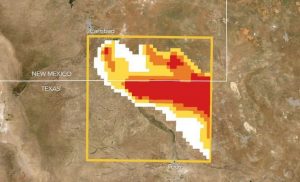
 Two fundamentally different methods EDF is using to measure and understand methane emissions in the Permian Basin are producing strikingly similar results. The mutually reinforcing sets of data — one gathered using aircraft, the other by satellite — each show that oil and gas operators in the region are releasing more than 3.5% of the natural gas they extract from the ground into the atmosphere as methane pollution.
Two fundamentally different methods EDF is using to measure and understand methane emissions in the Permian Basin are producing strikingly similar results. The mutually reinforcing sets of data — one gathered using aircraft, the other by satellite — each show that oil and gas operators in the region are releasing more than 3.5% of the natural gas they extract from the ground into the atmosphere as methane pollution.
That’s roughly twice the average rate found in 11 other major U.S. oil and gas basins. The wasted gas in the Permian is enough to supply 2 million American homes for a year.
The first of these efforts is EDF’s year-long PermianMAP, which tracks emissions from the ground and in the air, and takes the unprecedented step of publishing data online in near-real time to help industry and officials reduce those emissions, while letting the public see the results. The other is the first peer-reviewed scientific study to take direct measurement of Permian emissions, using the European Space Agency’s TROPOMI instrument.














