Midwestern states have traditionally been reluctant to embrace cap and trade. Now it looks like they may well turn into some of the larger beneficiaries of the California cap-and-trade system.
The largest supplier of likely carbon offsets for the California program so far? Arkansas.
Midwestern suppliers
Besides California and New York, numbers 2 and 3 on the list, none of the other states currently have cap-and-trade systems in place.
Michael Wara has a terrific blog post on this phenomenon and the ensuing politics of cap and trade. [Update: New graphs and data. The story doesn’t change. The graphs are prettier, though.]
Of the four types of offsets initially allowed in California (landfills, livestock, conservation forestry, and domestic ozone depleting substances), Midwestern states are the main beneficiaries.
Not CDM
How will that change the politics?
The Clean Development Mechanism (CDM), the UN-brokered international offsets system has perverse incentives. It motivates companies supplying large amounts of CDM credits (and receiving billions of dollars in return) to lobby their governments against instituting stricter domestic policies and having cap-and-trade systems on their own, lest they lose their chance of selling exactly those CDM credits. That’s one of the many reasons why the CDM system ought to be radically reformed.
What makes all the difference here is that CDM credits originate mainly from industrial and energy sectors that ought to be part of domestic cap-and-trade systems in the first place. California’s offsets are focused on sectors not covered by its own cap-and-trade system and most likely not covered directly in a US-wide emissions market.
A US-wide cap-and-trade system would only increase demand for these kinds of agricultural offsets and those from ozone depleting substances (ODS), making selling them even more attractive.
That by itself may not revolutionize federal politics, but at least the incentives are working in the right direction. Read More











 Yesterday’s New York Times published three terrific op-eds worth a second thought.
Yesterday’s New York Times published three terrific op-eds worth a second thought.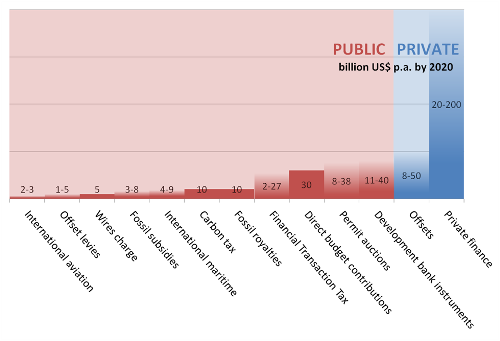
 His group Repower America launched
His group Repower America launched  The Chicago Climate Exchange, one of the first voluntary cap-and-trade programs, is shutting down next month. That’s bad news for the planet, isn’t it? Just take a look at today’s Wall Street Journal editorial page for an apparent confirmation. There the news is being celebrated as “cap and retreat.” Check.
The Chicago Climate Exchange, one of the first voluntary cap-and-trade programs, is shutting down next month. That’s bad news for the planet, isn’t it? Just take a look at today’s Wall Street Journal editorial page for an apparent confirmation. There the news is being celebrated as “cap and retreat.” Check.