Methane pollution from the oil and gas industry is a serious problem for our climate and communities, but it’s one most people aren’t even aware of. That’s because, while methane is a powerful pollutant, it is colorless, odorless and invisible to the naked eye.
But residents of Southern California’s Porter Ranch neighborhood had their eyes opened wide to the methane problem when a natural gas storage well in nearby Aliso Canyon ruptured and created a massive leak right next to their homes – an incident detected by residents in October from the putrid smell of mercaptan, an additive utilities use to more easily detect natural gas leaks.
Natural gas is made mostly of methane, and when it is released unburned, it has a warming power over 84 times that of carbon dioxide over 20 years. So, leaking or intentionally emitting unburned natural gas – which happens not just through malfunctions but often during routine production and transportation of oil and gas – can do major climate damage. The California Air Resources Board estimates that Aliso Canyon is pumping out methane at about 50,000 kg per hour, or about 62 million standard cubic feet, per day – that’s the same 20-year greenhouse gas impact as the daily emissions from 7 million cars.
Now, on day 48 in a very uncertain timeline of the one of the largest U.S. natural gas leaks ever recorded, infrared cameras are giving us a true glimpse at the size of this man-made methane volcano. Looking at side-by-side images of Aliso Canyon taken on Dec. 9 using an everyday camera and one equipped with infrared technology reveals just how blind we are to this kind of pollution:
 Read More »
Read More »
 After more than four months of spewing potent methane pollution, the massive Aliso Canyon gas leak has finally been plugged. But now the state of California and the utility that owns the site, SoCalGas, are left with the responsibility of ensuring a disaster like this doesn’t happen again.
After more than four months of spewing potent methane pollution, the massive Aliso Canyon gas leak has finally been plugged. But now the state of California and the utility that owns the site, SoCalGas, are left with the responsibility of ensuring a disaster like this doesn’t happen again.
 Southern California is now in month three of one of the country’s worst environmental disasters. In October 2015, a natural gas storage well operated by SoCal Gas sprung a massive leak hundreds of feet underground, releasing nearly 1,400 tons of gas into the air each day at its peak. Thousands of local residents impacted by noxious fumes and oily mist have been evacuated from the communities around the Aliso Canyon storage field. Because the leak is so large and technically complex, SoCal Gas has been working for months to fix it – so far without success.
Southern California is now in month three of one of the country’s worst environmental disasters. In October 2015, a natural gas storage well operated by SoCal Gas sprung a massive leak hundreds of feet underground, releasing nearly 1,400 tons of gas into the air each day at its peak. Thousands of local residents impacted by noxious fumes and oily mist have been evacuated from the communities around the Aliso Canyon storage field. Because the leak is so large and technically complex, SoCal Gas has been working for months to fix it – so far without success.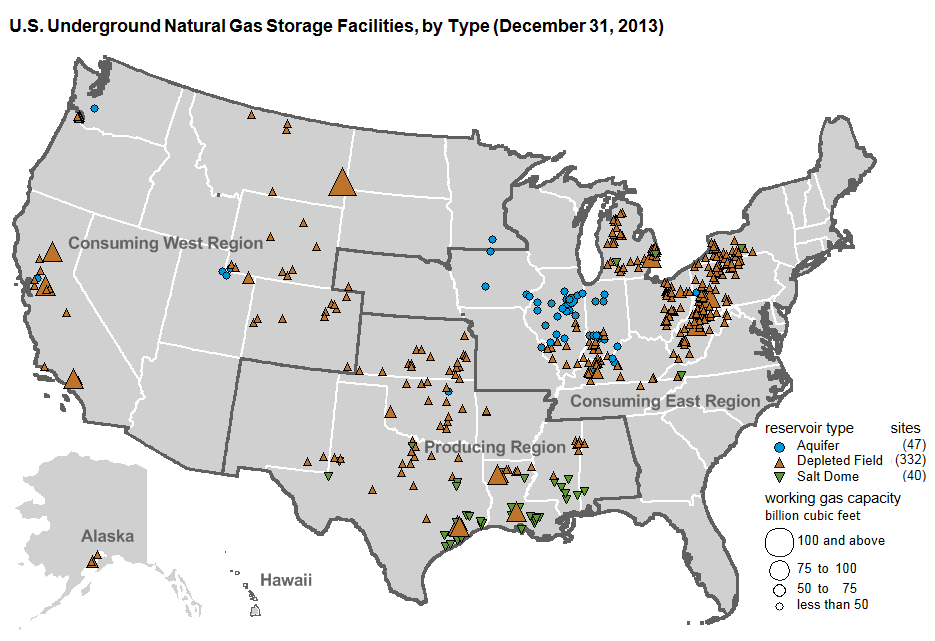
 No one likes uncertainty, least of all investors. From changes in interest rates, to supply chain disruptions, the list of risks investors must monitor is long and growing. Good, actionable information is investors’ most important tool for risk management and integral to successful investing. Without proper data, investors are flying blind.
No one likes uncertainty, least of all investors. From changes in interest rates, to supply chain disruptions, the list of risks investors must monitor is long and growing. Good, actionable information is investors’ most important tool for risk management and integral to successful investing. Without proper data, investors are flying blind.