The European Union’s methane regulation, set to begin reporting requirements this May, is a landmark step in climate policy. By targeting methane — a potent greenhouse gas responsible for a third of global warming – these rules reinforce Europe’s climate commitments and set a global standard for methane emissions reductions.
Energy Exchange
Strong oil & gas methane rules are essential — and achievable
Study suggests LNG production facilities should monitor methane emissions – just like the rest of the gas supply chain
By James France
Many parts of the world are looking to liquefied natural gas to provide a pathway to a cleaner and more secure energy resource — interest that has only grown since Russia’s war on Ukraine has shaken global energy markets. Meanwhile, gas-producing countries see LNG as a critical growth opportunity. The question is what an LNG boom would mean for the climate and communities near LNG facilities.
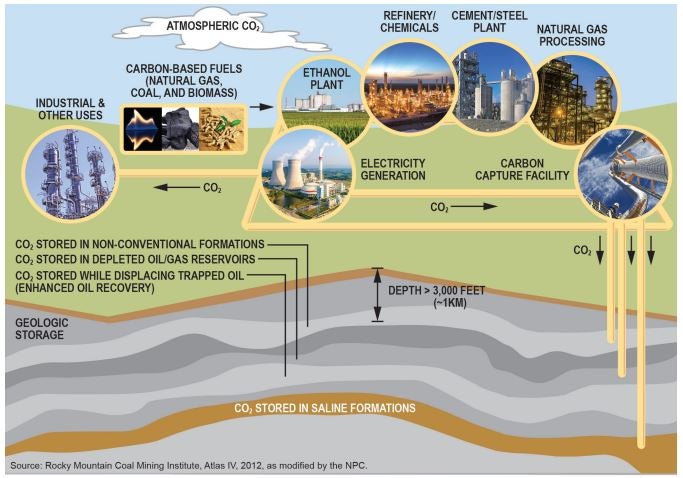
What DOE should consider as it makes decisions on Carbon Capture and Storage Demonstration Projects
 By Jona Koka
By Jona Koka
Nearly $5 billion from the Department of Energy combined with the economic incentives in the Inflation Reduction Act represent the United States’ first major steps to building a domestic carbon management industry that supports our Paris commitments.
States should not weaken liability laws for CCS projects
 Early this January, a geyser in West Texas started spewing tens of thousands of barrels of salty water a hundred feet into the air and coating the nearby land with salt deposits. It took about 10 days to discover the culprit was an old, dry oil well plugged in 1957 by Gulf Oil. By the next day, the Texas Railroad Commission had turned over the blowout and remediation to Chevron (who acquired Gulf Oil in the 1980s), who assumed full responsibility immediately and without question.
Early this January, a geyser in West Texas started spewing tens of thousands of barrels of salty water a hundred feet into the air and coating the nearby land with salt deposits. It took about 10 days to discover the culprit was an old, dry oil well plugged in 1957 by Gulf Oil. By the next day, the Texas Railroad Commission had turned over the blowout and remediation to Chevron (who acquired Gulf Oil in the 1980s), who assumed full responsibility immediately and without question.
This is a normal cost of doing business in the oilfield in Texas and elsewhere — you break it, you pay for it.
Traditional regulatory and legal principles around liability are designed to hold operators accountable when they or those they are responsible for fail to live up to their responsibilities. Such rules encourage operators to do as good and thorough a job as technically feasible.
However, some states are weakening these rules for operators of carbon sequestration and storage projects. If this quiet trend continues, the integrity of these projects, their climate benefits and their public acceptance could be significantly threatened.
Tax credits for carbon capture? Not without these 3 important rules.
By Adam Peltz and Scott Anderson
Removing carbon emissions from the air — a process known as carbon capture, utilization and sequestration — is one of the most important things we can do to battle climate change, and the Internal Revenue Service is currently developing regulations around tax incentives that could make or break the success of U.S. efforts to do this effectively.
CCUS is a suite of technologies that can capture carbon dioxide from the air and industrial sources. Companies can either reuse carbon dioxide or permanently store it in deep underground rock formations. The International Energy Agency estimates that by 2050, 9% of all necessary climate mitigation will come from CCUS activities. In other words, most versions of a carbon neutral economy will include a healthy amount of capturing carbon dioxide and putting it underground.
But CCUS can be a climate solution only if the carbon is securely stored once removed from the atmosphere. Any regulation or tax incentive offered to companies who practice CCUS must assure that.