Tom Neltner, J.D., is Chemicals Policy Director and Dr. Ananya Roy is Health Scientist
Last week, we noted in our blog that the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) dropped the statement that paint, dust and soil are the most common sources of lead in its “Protect Your Family from Lead in Your Home” booklet. Property owners provide this booklet to prospective homebuyers and tenants in housing built before 1978. The change implicitly recognizes that there is no safe level of lead in the children’s blood, and we must reduce all sources of lead exposure. It also acknowledges that the relative contribution of air, water, food, soil, dust, and paint to children’s blood lead levels is complicated. Exposure varies significantly based on age of the home, the child’s race and age, the family’s income-level, and region of the country. Any simplification obscures these important differences.
EPA’s scientists made this clear in a model published earlier this year that pulled together the available data, divided children into three age categories, and assigned children in each category into ten groups based on their overall lead exposure. For each group, they estimated the relative contribution of air, water, food, and soil/dust (from paint). Not surprisingly, children living in older homes with lead-based paint hazards by far have the most exposure to lead. For 1 to 6 year olds in the top 90-100 percentile, more than 70% of the lead in their blood is from soil and dust. The contribution from food is 20% and drinking water is 10%. For infants, soil and dust contributes to 50% of the lead in blood, while 40% is from water and 10% from food.
Since there is no known safe level of lead in blood, we must do even more to reduce children’s exposure to lead-contaminated soil and dust.
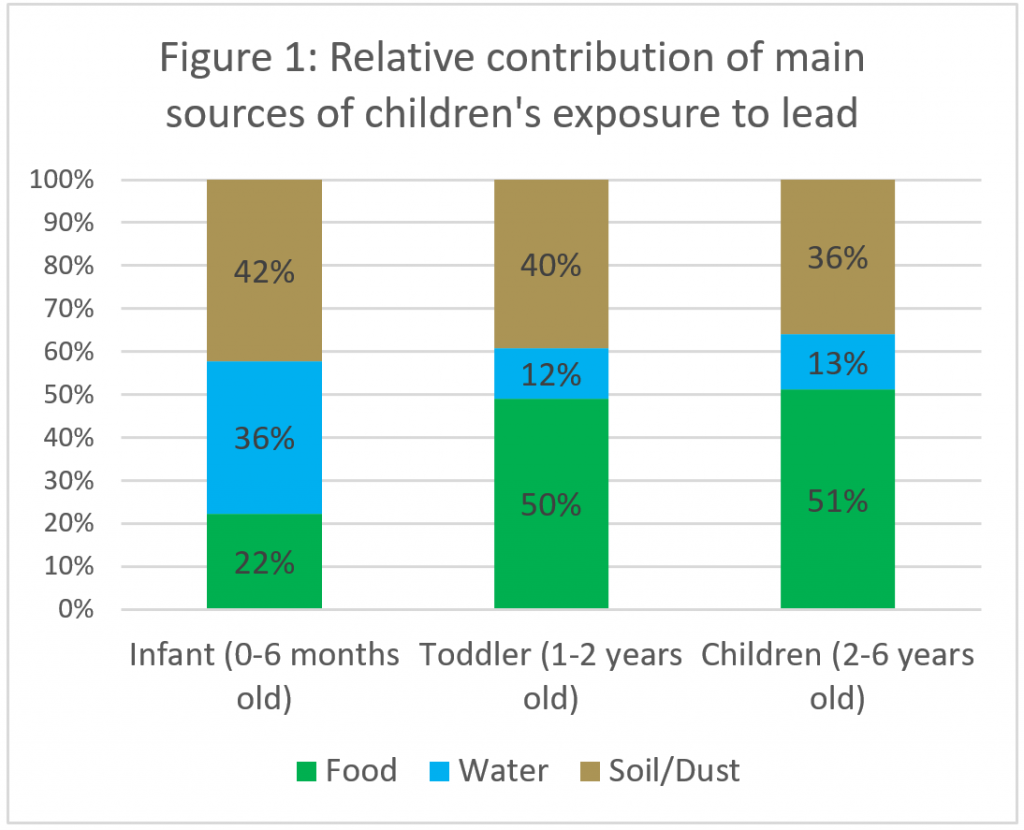 However, to prioritize action at a national level, it is important to understand how different sources contribute to lead exposure in the average child as well as the most-exposed child. We used the underlying EPA data to calculate the average relative source contribution of different sources to blood lead levels for infants from birth to six months old, for toddlers 1 to 2 years old, and young children from 1 to 6 years old. The results indicate that infants have a much higher source contribution of lead from water in comparison to older children (Figure 1). For the average child 1 to 6 years old, food is the largest source of lead exposure, with 50%, followed by soil/dust then water.
However, to prioritize action at a national level, it is important to understand how different sources contribute to lead exposure in the average child as well as the most-exposed child. We used the underlying EPA data to calculate the average relative source contribution of different sources to blood lead levels for infants from birth to six months old, for toddlers 1 to 2 years old, and young children from 1 to 6 years old. The results indicate that infants have a much higher source contribution of lead from water in comparison to older children (Figure 1). For the average child 1 to 6 years old, food is the largest source of lead exposure, with 50%, followed by soil/dust then water.
Read More »
 The Childhood Lead Action Project was founded in 1992 to take on this challenge, with the mission of eliminating childhood lead poisoning in Rhode Island through education, parent support, and advocacy. The organization does it all: workshops and educational outreach for a wide range of audiences, municipal and state-level advocacy to push proactive policies, grassroots campaigning, and more.
The Childhood Lead Action Project was founded in 1992 to take on this challenge, with the mission of eliminating childhood lead poisoning in Rhode Island through education, parent support, and advocacy. The organization does it all: workshops and educational outreach for a wide range of audiences, municipal and state-level advocacy to push proactive policies, grassroots campaigning, and more.











