By Lauren Ellis, MPH, Research Analyst, Safer Chemicals
What’s New: A peer-reviewed study by Danish researchers found that a male fetus who is exposed to PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances—also known as “forever chemicals”) during early pregnancy is more likely to have lower sperm quality in early adulthood.
It’s the first study to explore the impact of exposure to more than two PFAS compounds (as measured in maternal blood samples during early pregnancy) on adult male reproductive hormones and sperm quality.
Why It Matters: Poor sperm quality is directly related to male infertility. In addition, it has been linked to other health problems such as testicular cancer, heart disease, and all-cause mortality.
This study adds to decades of literature linking environmental chemical exposures to negative impacts on reproductive health.
Key Lessons from the Study:
- Women who were pregnant 20+ years ago had multiple types of PFAS in their blood. The study used data on a group of Danish women who were pregnant between 1998-2003. The women gave blood samples, which were then frozen and stored; 95% of those samples were taken in the first trimester of pregnancy.
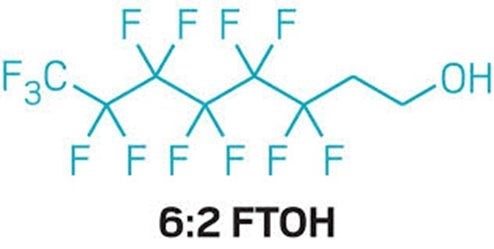
- In 2020-2021, researchers tested those maternal samples for 15 different PFAS compounds. They found 7 of the 15 in the bloodstream of nearly 90% of mothers in the study. The seven were: PFHxS, PFHpA, PFOA, PFOS, PFNA, PFDA, and PFUnDA.
- Exposure to PFAS during pregnancy decreases the sperm quality of adult male offspring. Researchers found that both combined and single exposure to maternal PFAS concentrations during early pregnancy had a negative effect on the sperm quality—particularly sperm count, concentration, and movement—of adult male offspring.
Our Takeaway: The new study presents a startling finding—developmental exposures to chemicals are associated with long lasting harm, including impacts that can affect future generations. It also adds to the growing evidence of PFAS health risks and demonstrates the urgent need for more health-protective PFAS policies and regulations.
Next Steps: EDF and our partners are pushing EPA to revoke existing PFAS exemptions and require those PFAS (and new PFAS coming to market) to undergo a full safety review under the Toxic Substances Control Act, our nation’s primary chemical safety law.
It is critical that these evaluations also consider the cumulative risk of exposure to PFAS mixtures in the environment.
Note: In June 2021, EDF, with a group of health, environmental, and consumer organizations, sent a formal petition to FDA asking the agency to ban all PFAS that accumulate in the body. That petition is still under review.