Tom Neltner, J.D., Chemicals Policy Director, and Maricel Maffini, Ph.D., Independent Consultant
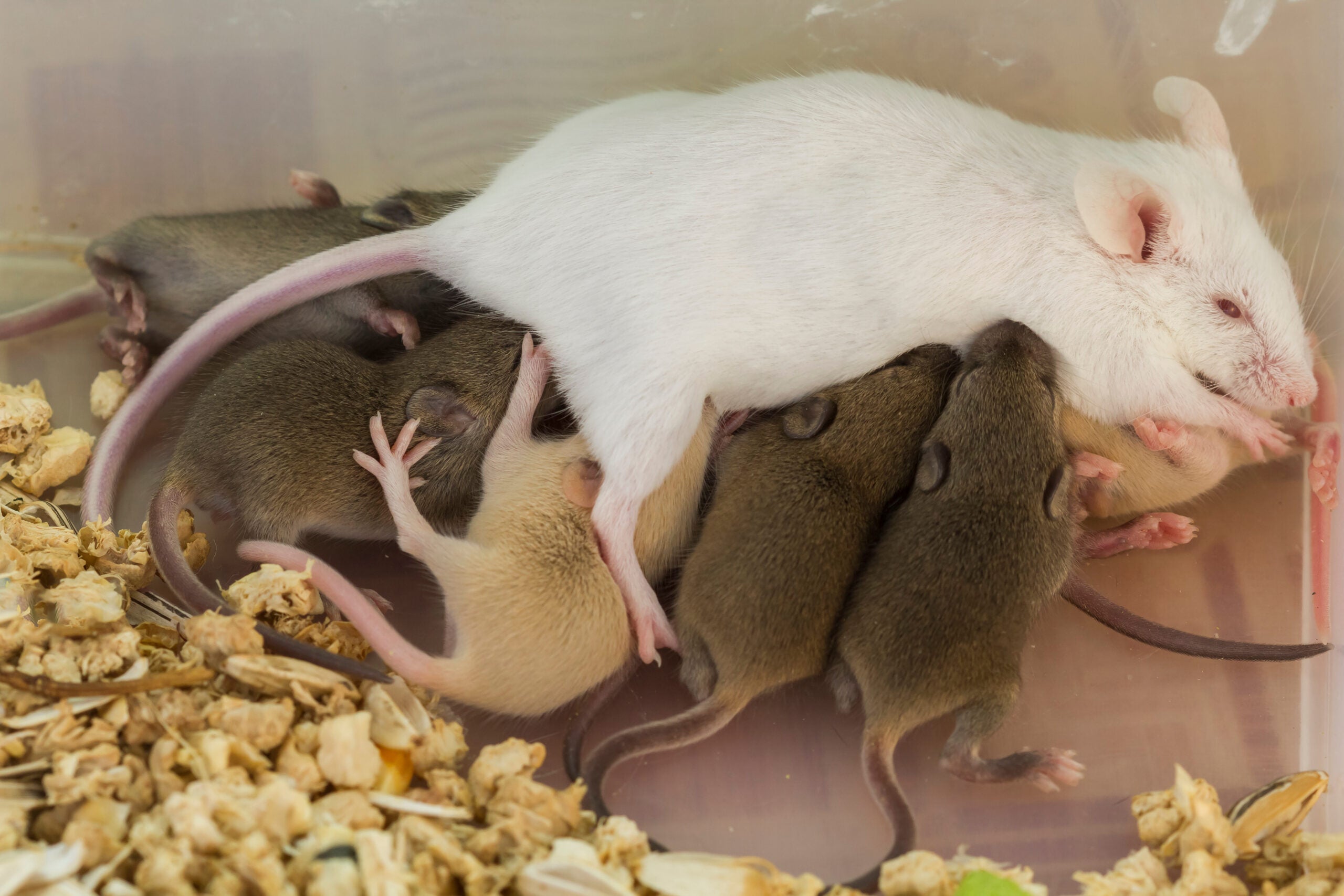
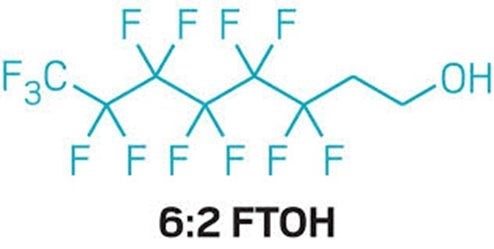
This blog is the fourth in a series describing information we discovered in reviewing thousands of pages from the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) response to our Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) of the agency’s approval of 31 Food Contact Substance Notifications (FCNs) from 2002 to 2016 submitted by six companies for 19 distinct chemical mixtures of per- and poly-fluorinated substances (PFAS).
In this blog, we identify one company’s serious breach of its obligation to provide FDA with all relevant toxicology data. While hindsight is 20/20, we have reason to believe that if FDA had had all relevant information, it would have demanded more studies potentially revealing risks that are only now coming to light with related chemicals. Though we have not completed a similar review for the other companies, we think this inadequate approach to chemical safety is not unique to a single company, and FDA should reassess all its reviews given what is now known about PFAS chemicals.
Safety assessment requirements for food additives – including food contact substances
When a company seeks FDA’s approval of food additives (including food contact substances), it is required to provide the agency with all relevant chemistry, toxicology and environmental data so it can conduct a safety assessment. While the agency typically conducts a literature search of its own and of public databases, the company that is claiming the chemical’s use is safe is obligated to include any data that is inconsistent with the company’s conclusion.
Read More »