Tom Neltner, J.D., is Chemicals Policy Director
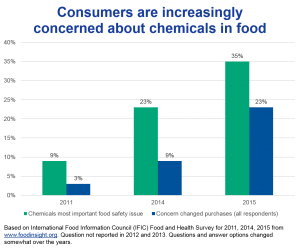
Since 2014, chemicals in food[1] have been consumers’ most important food safety issue, reaching a high of 35% in 2018, according to annual industry surveys by the International Food Information Council. For comparison, “foodborne illness from bacteria” was half that percent.
Food companies have responded to this growing consumer alarm by adopting policies banning artificial flavors, colors and other ingredients that sound like chemicals. This approach is unlikely to do more than serve as window dressing for the underlying problems since it’s not science-based – many of these additives may be safe. The Center for Science in the Public Interest called out this practice in its 2017 “Clean Label: Public Relations or Public Health?” report and pointed readers to its Chemical Cuisine system that rates common additives for health and safety.
There are some companies, like Panera Bread, that are taking a more systematic approach to the ingredients used in the food they sell, starting with the question of whether the additives used are essential and whether the ingredients pose health or safety concerns. As a result, the company worked closely with their suppliers and reformulated many of their products.
And now, thanks to a fascinating new report from the Environmental Working Group (EWG), we are learning about another structured approach that addresses health concerns with chemical additives – the Federal organic certification program for processed foods. To be honest, before reading the report, I viewed the organic program as narrowly focused on pesticides and was only vaguely aware of how it dealt with chemical additives. I was missing the bigger picture.