Th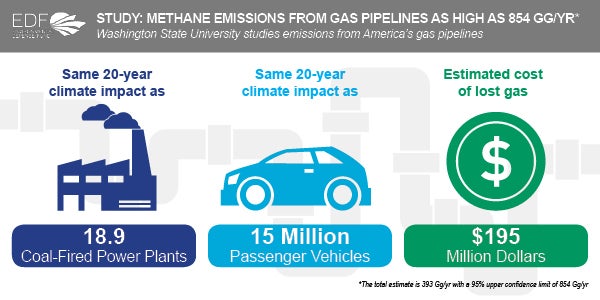 e most important takeaway from a study released today by Washington State University (WSU) is that despite improvements, large amounts of methane continue to leak from the nation’s local natural gas systems. Because methane is a particularly potent greenhouse gas, these yearly emissions are comparable to the CO2 from as many as 19 coal-fired power plants.
e most important takeaway from a study released today by Washington State University (WSU) is that despite improvements, large amounts of methane continue to leak from the nation’s local natural gas systems. Because methane is a particularly potent greenhouse gas, these yearly emissions are comparable to the CO2 from as many as 19 coal-fired power plants.
The estimated value of the gas escaping each year, by the way, is up to $195 million.
Although these figures represent a major ongoing challenge for gas utilities, they do reflect substantial improvement over the past two decades, thanks to a combination of effort and investment by utilities, along with a series of both state and federal policy changes enacted since 1992.
The new findings reinforce the fact that when regulators and companies both set their minds to fixing a problem, they can get some pretty good results. Methane, the primary component of natural gas, is a particularly powerful climate warmer – 84 times more potent than carbon dioxide over the first 20 years after it is released to the atmosphere.
While they remain a serious problem, the ongoing utility emissions also represent an important opportunity for companies and regulators to make a big dent in greenhouse pollution. EDF believes the study underscores three major areas where improvement is necessary: Read More










 With the Environmental Protection Agency’s
With the Environmental Protection Agency’s 