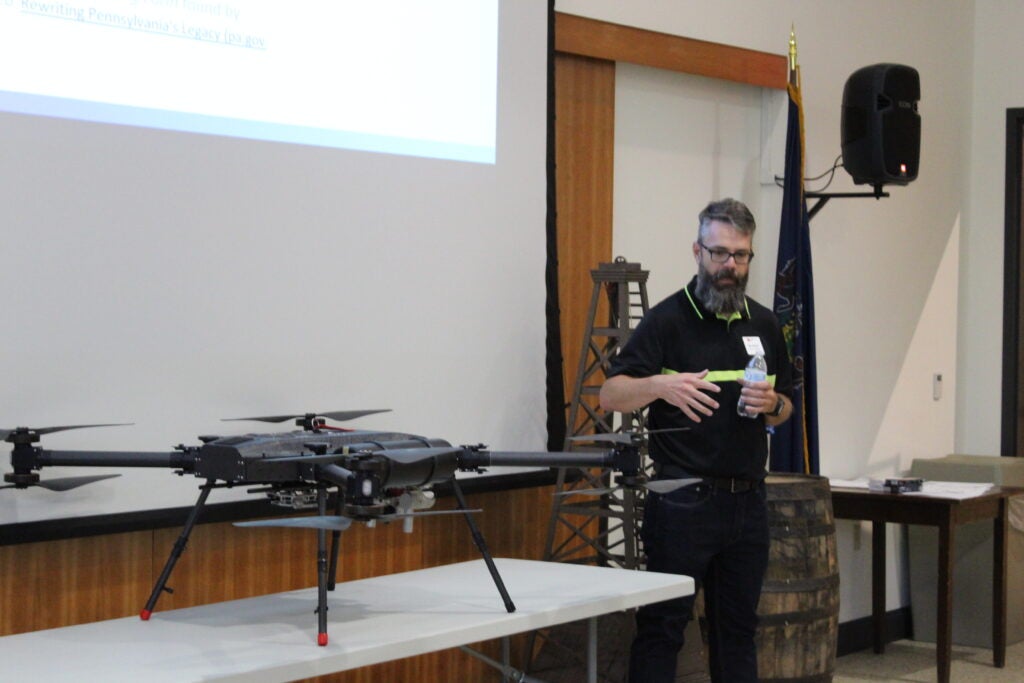
There are at least a million dead and forgotten oil and natural gas wells dotting the American landscape, many leaking methane and other toxic chemicals into the air and water, long after their productive days are over. In Pennsylvania alone, there are an estimated 300,000 to 700,000 — and estimated is the key word. The fact is, nobody knows. But we do know that thousands of landowners have these ownerless orphan wells on their property, often without knowing it. The first step to solving a problem like this is to locate it. So EDF, together with the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection, the Department of Energy, McGill University and Moms Clean Air Force has launched a project to locate and address hidden orphan wells in western Pennsylvania. Drone-mounted magnetometers and advanced methane detection technologies will be honing in on forgotten orphan wells in the area starting in October and November.
Energy Exchange
Flying over Pennsylvania in search of orphan wells: building momentum to solve a global problem
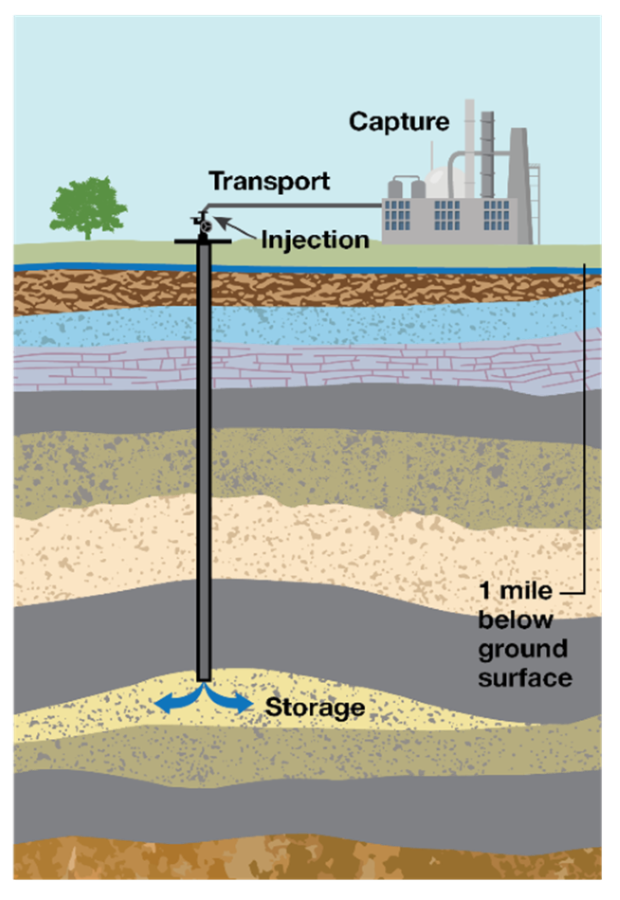
Carbon dioxide injection wells require deliberate and protective liability rules
Post-closure liability management may be a rather obscure part of the burgeoning carbon capture and sequestration , or CCS, industry. But more and more lawmakers and regulators in U.S. states and around the world recognize it’s an important piece of their climate change agenda.
New Mexico can protect its citizens by closing an orphan well loophole
By Adam Peltz and Meg Coleman
New Mexico’s legislators have a remarkable opportunity in the coming days to protect New Mexico families, businesses and the environment by revising the antiquated Oil and Gas Act with House Bill 133.
New study shows need for accurate methane measurement at orphan oil wells and throughout industry
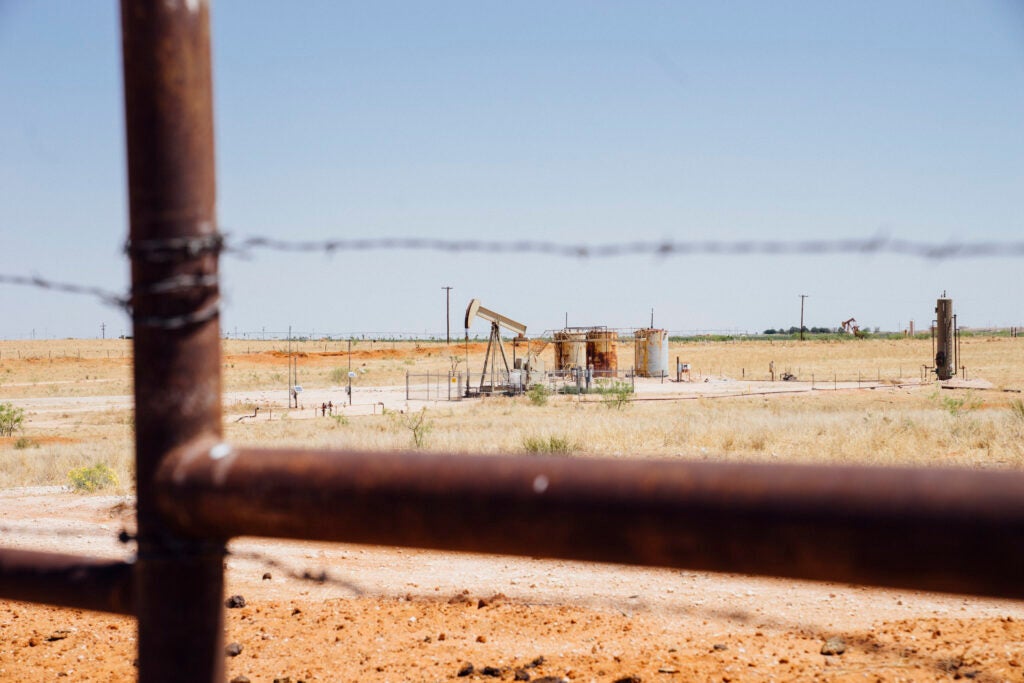
New research from Colorado State University reveals significant quantities of methane leaking from the state’s orphaned oil and gas wells — an urgent problem for the state to address as the number of abandoned oil and gas wells have surged in recent months. This study underlines the importance of both the state’s efforts to plug and remediate orphan wells as well as the efforts underway at the state Air Pollution Control Division to better understand and quantify methane emissions from oil and gas wells in the production sector.
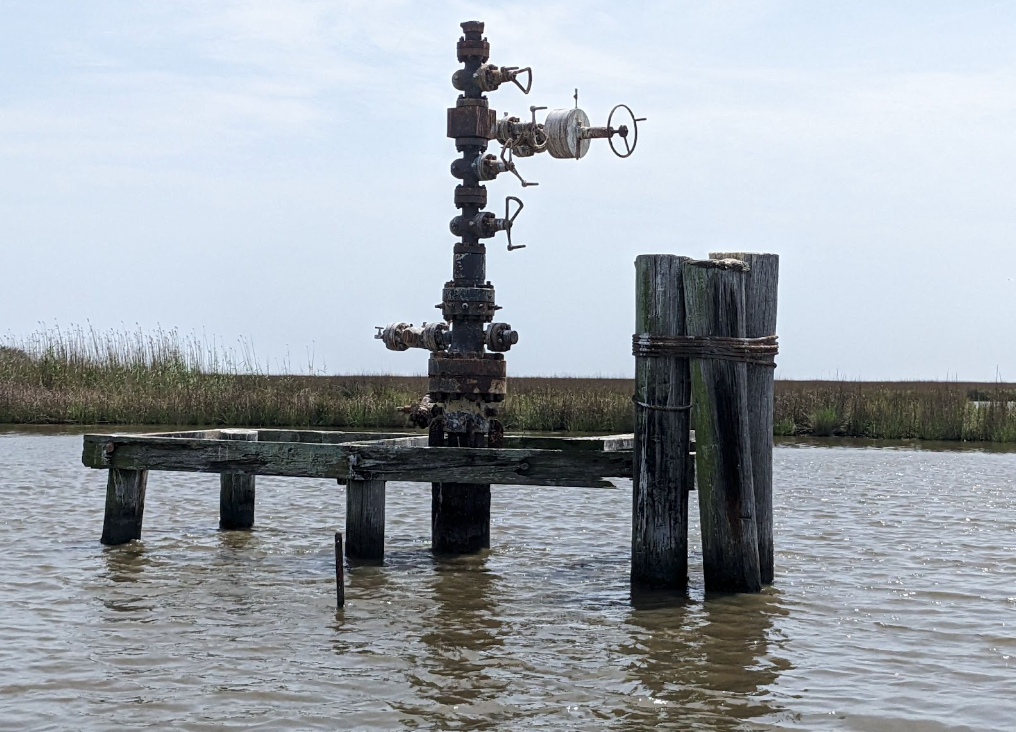
New Louisiana rule will plug old oil wells, create jobs, safeguard environment
The Louisiana Department of Natural Resources has finalized new rules to help improve management of 17,000 non-productive oil and gas wells by encouraging their proper closure —an action that will create jobs, raise property values across the state and facilitate new clean energy projects.
Louisiana has a long history of oil and gas development, with 50,000 wells distributed across the state and along the coast. The state has a responsibility to ensure none of these wells become an environmental or economic liability.
About a third of these wells are non-producing but registered as having future utility, meaning the operator claims that they could be economically productive in the future. As a result, the operator isn’t required to plug the well. However, once wells are idled for more than three years, just one in five ever return to service. Often they will only see a tiny fraction of their former production levels.
Unplugged wells cause a host of economic, environmental and even public health and safety problems. They can leak methane and toxic air pollution, contaminate water, reduce property values and prevent other economic uses of the land.
New maps unveil scale of U.S. orphan well challenge, highlight solutions at hand
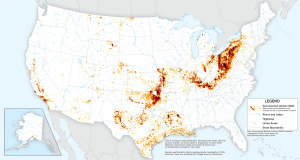 Last year, for the first time, EDF and McGill University mapped every existing documented orphan well across our country. Shortly after, Congress passed the Infrastructure and Investment Act, IIJA, which included $4.7 billion to document, plug and remediate orphan wells. This new funding, secured through EDF’s leadership, provides federal support for the first time for states, Tribes, and federal land management agencies to find and plug orphan oil and gas wells that are inactive and unplugged with no solvent owner of record.
Last year, for the first time, EDF and McGill University mapped every existing documented orphan well across our country. Shortly after, Congress passed the Infrastructure and Investment Act, IIJA, which included $4.7 billion to document, plug and remediate orphan wells. This new funding, secured through EDF’s leadership, provides federal support for the first time for states, Tribes, and federal land management agencies to find and plug orphan oil and gas wells that are inactive and unplugged with no solvent owner of record.
Prior to this legislation, states, which oversee 90% of the wells in the country, had a fraction of the funding needed to plug wells with the unfortunate result that they often sat unplugged for decades. Now, we’re publishing an updated orphan wells map that draws on newly available data to offer decision makers and the public a clearer picture of the issue.