FDA says “Cookware that exhibits any level of leachable lead upon testing is prohibited.”
What’s New?
For the first time, FDA has provided guidance on how to evaluate whether metal cookware is prohibited due to lead leaching into food.
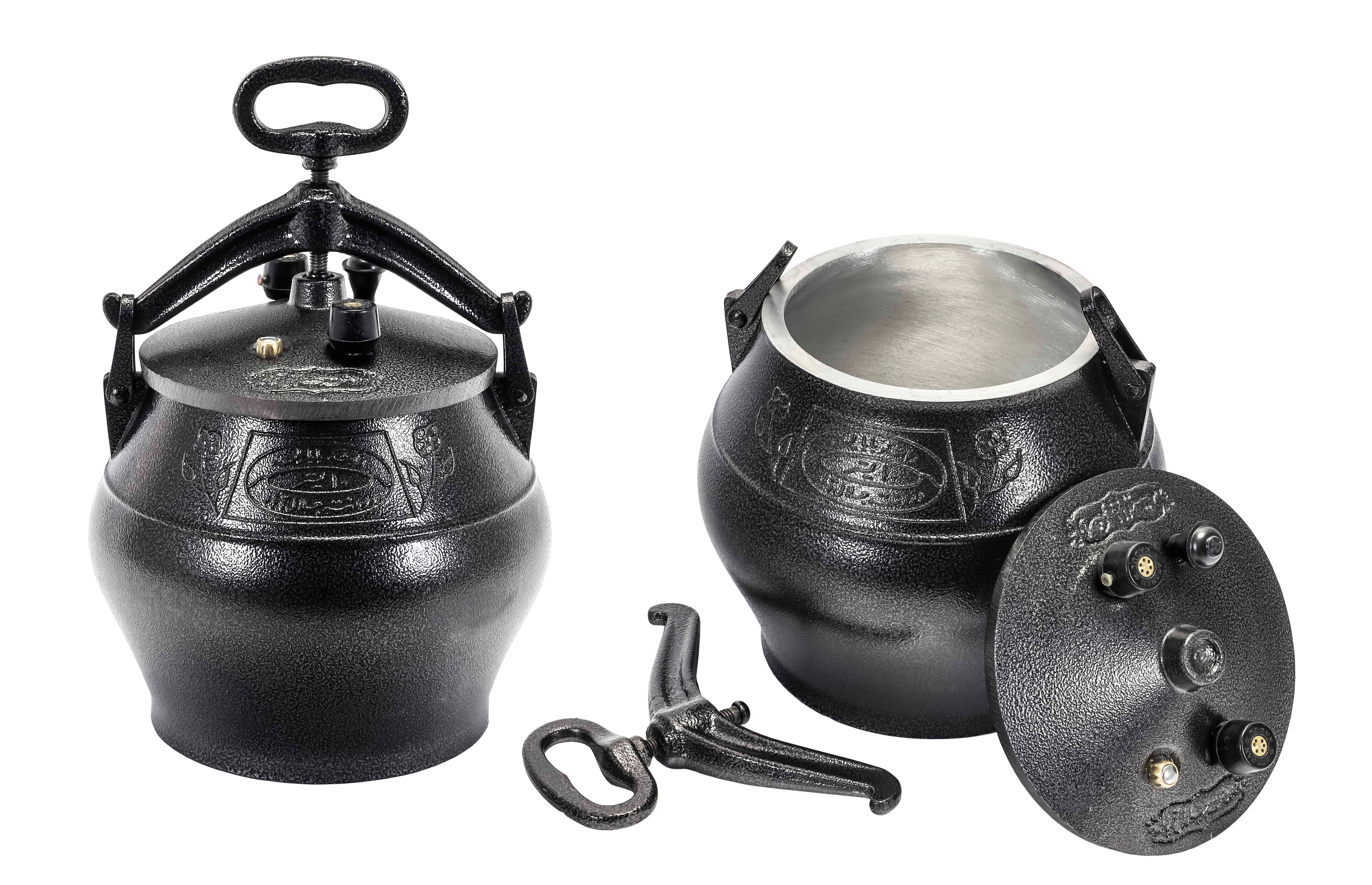
As part of an investigation to find the source of elevated blood lead levels in some refugee children, the Hazardous Waste Management Program in King County, Washington [1] encountered high lead levels in certain imported [2] aluminum cookware, including pressure cookers and pots & pans. The program attempted to bring this to FDA’s attention in late 2019, and submitted a formal product report to FDA in October 2021, after several attempts to contact an FDA representative directly.
In May 2022, the Program published a journal article about its findings; a year later, staff emailed FDA again seeking guidance. On June 1, 2023, FDA responded with a letter [PDF, 166KB] providing a method (see below) to evaluate lead in metal cookware. The agency also said:
- “The marketing in interstate commerce, including importation, of cookware that exhibits any level of leachable lead upon testing is prohibited.”
- “Neither lead nor lead-containing materials (e.g., metals, solder) are permitted under FDA regulations for use in contact with food.”
- The Program should “feel free to share this letter or any of its contents with Amazon.com, Inc.,[3] and any other firms involved in the marketing or sale of cookware.”[4]
Why It Matters
There is no safe level of exposure to lead. Through its Closer to Zero program, FDA has committed to reducing children’s exposure to lead. That effort is primarily focused on lead as a contaminant in food and not in food contact materials containing lead that can leach into food or water. In many cases, the lead may be added, such as:
- Brass and bronze used in faucets and cookware;
- Tin alloys used to coat steel cans; and
- Aluminum alloys used in some imported cookware, especially cookware made in countries with weak regulatory programs.

In December 2020, EDF and 11 other organizations filed a citizen petition with FDA documenting the problem and asking the agency to prohibit the intentional addition of lead, and to tighten the limits on contaminants more generally. Supporting comments from more than 50 organizations provided additional documentation. FDA has not yet made a decision on that petition.
FDA’s Method for Evaluating Metal Cookware
In providing guidance for evaluating metal cookware, FDA modified an existing method “ [PDF, 1.35MB] designed for silicate-based materials, such as earthenware, ceramicware, and lead crystal” used as foodware. To account for high temperatures in cookware, the agency said to boil vinegar (4% acetic acid) in the cookware for two hours, and then let it sit for a total of 24 hours and analyze the liquid for measurable amounts of lead.
FDA noted that the method has a measurable limit of 50 to 100 ppb for lead and that other methods have lower limits that “may be preferable to further reduce the risk of lead leaching into food from cookware.”
Our Take
FDA’s letter provides long-overdue guidance on how to evaluate lead in metal cookware. The information will help industry comply with its responsibilities not to sell adulterated cookware. It will be particularly helpful to state and local health departments that are on the front lines of protecting children from lead, especially as they investigate cases of children with elevated blood levels.
We applaud both the Hazardous Waste Management Program and the FDA, the former for its investigations and outreach to the FDA, and the latter for its clear response. Strengthening the critical lines of communication among public health agencies will help protect children and make food, cosmetics, and other products safer for all.
However, FDA’s letter raises a number of questions that should be addressed:
- Why did FDA not make the letter publicly available on its website? We learned of it through a posting by the Hazardous Waste Management Program on a listserv for lead-poisoning prevention. Making the letter public could increase awareness of the issue and prevent harmful lead exposures.
- Is FDA engaging with marketplaces and their vendors directly to keep similar adulterated food contact materials off the market? The agency recently updated a long-standing import alert for ceramicware due to lead or cadmium. On August 9, 2023, it issued an import alert for one brand of pressure cooker, but the problem appears to go beyond just one brand.
- Why did FDA recommend the method for evaluating metal cookware that it did, rather than a more sensitive method that it has validated to measure lead in food and food ingredients? According to the Baby Food Council, 13 labs have demonstrated proficiency measuring to at least 6 ppb of lead with this method.
- Why has the agency still not acted on the December 2020 citizen petition that requested the agency prohibit lead as an additive in brass, bronze, and other food contact materials?
Next Steps
EDF and our allies focused on protecting children from harmful lead exposure will continue to push for FDA to act on lead, including considering our options to force the agency to finally address long-standing problems with lead in food contact materials raised by the citizen petition. We filed a FOIA request seeking the agency’s documents and other communications regarding lead in food contact materials, which may shed some light. We will also work with health departments and industry to find ways to drive lead exposure closer to zero.
NOTES
[1] The Program is a public partnership consisting of five partners: Public Health – Seattle & King County, King County Solid Waste Division, King County Water and Land Resources Division, Seattle Public Utilities and Sound Cities Association.
[2] High levels initially found in cookware from Afghanistan and later in products imported from other countries including India, China, Columbia, Pakistan and elsewhere according to the Program.
[3] Amazon was one of three on-line marketplaces that offered pressure cookers that the Program found to have high levels of lead.
[4] The letter does not define cookware, but it appears to be any foodware or other food contact material used to cook food or food ingredients.