 EDF, along with a coalition of health and environmental groups, just filed a motion to intervene in defense of vital new standards that will prevent the wasteful loss of natural resources, save money for taxpayers and tribes, and reduce emissions of dangerous and climate-disrupting pollution.
EDF, along with a coalition of health and environmental groups, just filed a motion to intervene in defense of vital new standards that will prevent the wasteful loss of natural resources, save money for taxpayers and tribes, and reduce emissions of dangerous and climate-disrupting pollution.
The Bureau of Land Management’s (BLM) waste prevention standards will reduce venting, flaring, and leakage of natural gas on BLM-managed federal and tribal lands – but they are being challenged in U.S. Federal District Court in Wyoming by oil and gas industry groups and three states.
Federal and tribal lands are an important source of oil and gas production. Together, the amount they produce is the equivalent of five percent of the U.S. oil supply and 11 percent of the U.S. natural gas supply, and generates more than $2 billion annually in royalties.
Unfortunately, oil and gas companies that lease these federal and tribal lands lose substantial amounts of publicly-owned natural gas through unnecessary venting, flaring, or leaking at production sites.
A recent study from ICF International found that in 2013, drilling on federal and tribal lands —mostly in the rural West— leaked, vented, and flared natural gas worth about $330 million. An analysis from the Western Values Project estimates taxpayers could lose almost $800 million over the next decade if wasteful venting and flaring practices continue.
In addition to wasting a public resource, oil and gas companies’ unnecessary venting, flaring, and leakage on federal and tribal lands also poses significant public health and safety risks.
The wasted natural gas is primarily composed of methane – a powerful greenhouse gas, capable of warming the climate at a rate 84 times that of carbon dioxide over a 20-year period.
The leaked, vented, and flared natural gas also emits air pollutants including carcinogens such as benzene, and volatile organic compounds – which contribute to hazardous smog.
BLM’s recently finalized venting and flaring standards deploy common sense, cost-effective, and readily available technologies — already effectively in use in several states across the country — to capture this gas.
The standards yield significant benefits by minimizing the waste of a taxpayer-owned natural resource, and by curbing emissions that contribute to air pollution and climate change, all while helping to create new jobs in methane mitigation. They will save, and put to productive use, up to 56 billion cubic feet of gas a year — enough to supply up to 760,000 households – and will provide millions in additional revenues for taxpayers.
The standards will also cut methane emissions by up to 169,000 tons per year — the equivalent to carbon emissions from as many as 890,000 vehicles.
These benefits will accrue to millions of people across the country, including those living near oil and gas development on federal and tribal lands.
EDF member and New Mexico rancher Don Schreiber has more than 100 oil and gas wells on and near his ranch in the San Juan Basin that will now be covered by the BLM standards. In a declaration supporting EDF’s motion to intervene, he describes the impact of venting, flaring, and leaking from these wells on his family and, in particular, his grandchildren:
Most noticeable is the near-constant smell from leaking wells. … These odors make breathing uncomfortable and often cause us to leave affected areas as quickly as possible. … We worry about [our grandchildren’s] exposure to air pollutants from oil and gas development on the property, and always are careful to keep them away from the wells and above ground pipeline equipment. Protecting our grandchildren from the negative health effects of oil and gas emissions is a constant concern when they come to visit us. (New Mexico rancher Don Schreiber, Declaration)
With the new standards, he anticipates a reduction in the “harmful air pollution near my home and in the state where my family and I live, work, and recreate.” (Declaration)
BLM’s efforts to reduce natural gas waste have broad and cross-cutting support from elected officials and community members across the West. In a recent bipartisan poll of Western states, 80 percent of respondents supported BLM standards to curtail waste of this valuable resource. And, over the course of several years during which the rule was under development, BLM solicited the feedback of community stakeholders, oil and gas developers, and local, tribal and state governments. The final rule is the result of a collaborative and deliberate process and includes changes that reflect this stakeholder input.
Standing in stark contrast to this careful process, industry associations rushed to file legal challenges seeking to overturn the waste prevention rule within 40 minutes after it was released — hardly enough time to read the rule, let alone meaningfully consider its contents.
And in a subsequent filing seeking to block these protections before they become effective, these industry associations put forward a number of flawed claims, not least of which was their suggestion that BLM acted unlawfully because its rule may “only” produce additional annual royalty revenues of $22.4 million — a sum the filing characterizes as “de minimis.”
While $22 million annually may be an insignificant amount for the oil and gas companies litigating to overturn this rule, it has real meaning for infrastructure projects, schools, and communities across the country that stand to benefit from this funding.
It’s unfortunate that some have engaged in reflexive efforts to roll back protections designed to prevent the waste of our nation’s public resources and, at the same time, protect our air quality and climate.
The good news is that BLM’s commonsense standards are firmly rooted in the agency’s manifest authority to minimize waste and to address the harmful health and environmental consequences of oil and gas development on federal lands. We at EDF look forward to vigorously defending these standards in court.
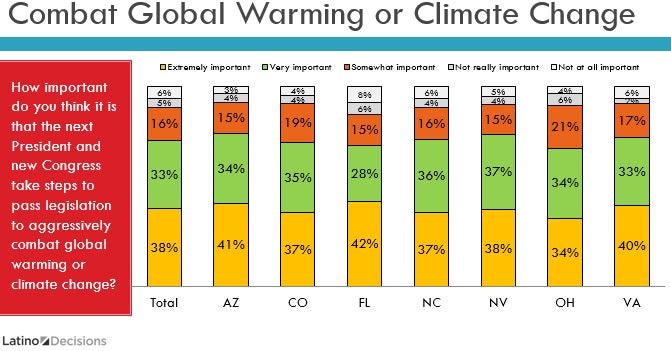










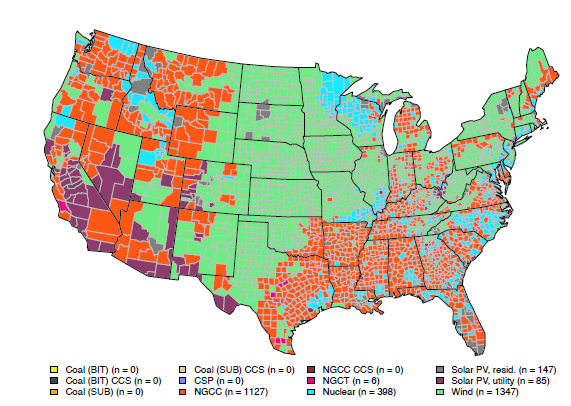
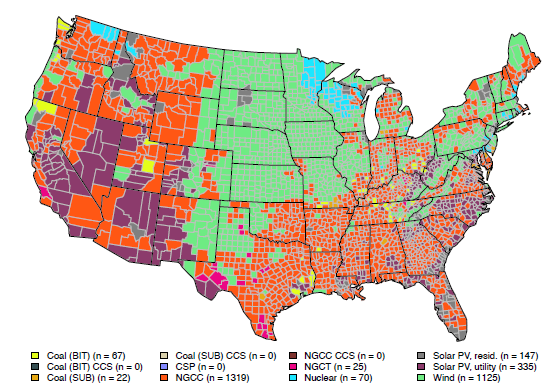
 EDF, along with a coalition of health and environmental groups, just
EDF, along with a coalition of health and environmental groups, just