The Mercury Standards, Post-Supreme Court – Still in Effect, Still Protecting Americans

The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) first proposed the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards back in 2011, at a news conference at Children’s Hospital with cheering children and families surrounding the speakers.
They were cheering because the Mercury Standards were the single most important clean air measure of our generation – designed to protect Americans from some of the worst, most dangerous types of air pollution.
They still are.
This week’s disappointing Supreme Court decision, remanding the standards back to the D.C. Circuit Court for further analysis, has distracted from that fact.
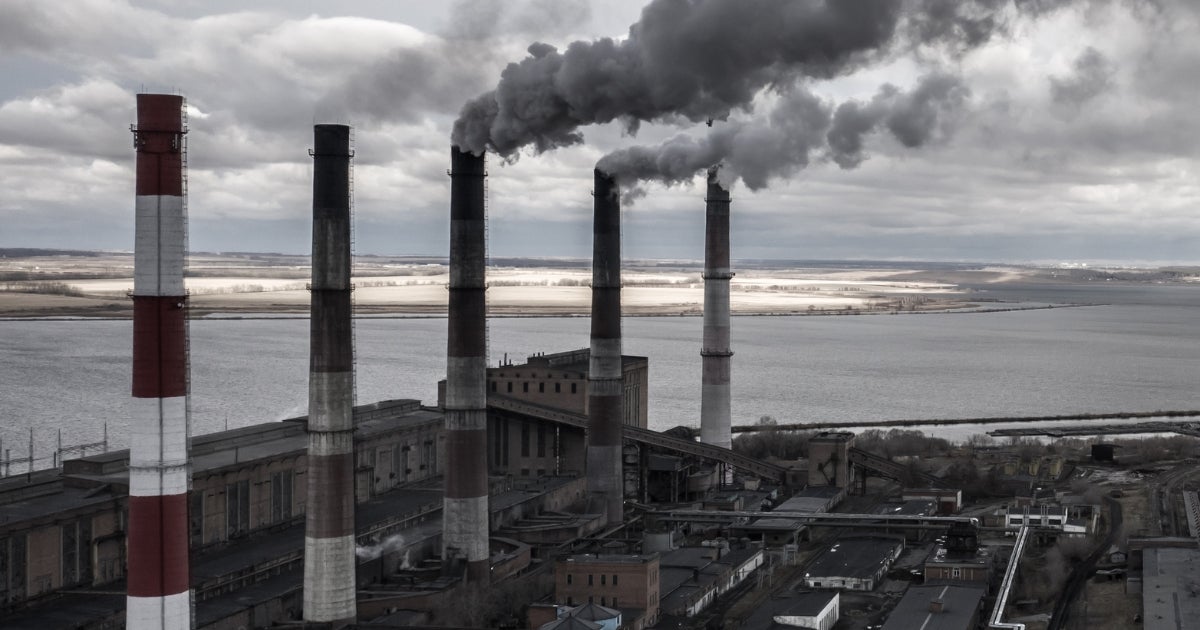
But the fact remains – the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards are a suite of life-saving protections against some of the most health-harming substances emitted by coal and oil-fired power plants, including mercury, arsenic and other heavy metals, and acid gases.
Here’s What Happened
Coal- and oil-fired power plants are by far the largest emitters of these pollutants, which are dangerous to human health even in small doses. Mercury causes brain damage in children, metal toxics like chromium and nickel cause cancer, and acid gases cause respiratory problems.
This week, the Supreme Court held that EPA should have considered the costs of regulation when it made a threshold determination under section 112 of the Clean Air Act that it is “appropriate and necessary” to move forward with the first-ever national limits for these noxious emissions. It is now up to EPA to determine the best way to respond to the decision.
(The case was Michigan v. EPA. EDF was a party to the case. You can read the decision and the sharp dissent here.)
What does the Supreme Court ruling mean for the Mercury Air Toxics Standards?
Here are three important things you should know.
First — there is every reason to believe EPA can quickly amend its “appropriate and necessary” finding to address the Supreme Court’s decision, without affecting the substance of the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards themselves.
Importantly, the Court left it up to EPA to determine how to evaluate costs and how to weigh those costs against the benefits of regulation. As the Court’s opinion acknowledged, EPA has already conducted an extensive review of both the costs and benefits of the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards as part of the regulatory analyses most agencies carry out under Executive Order 12866. That analysis contains overwhelming evidence showing that the benefits of MATS far outweigh its costs.
According to EPA, the monetized benefits of the Mercury and Air Toxics are expected to be up to $90 billion per year.
That amount reflects the enormous health benefits Americans will get from the standards. EPA estimates that they will prevent 11,000 premature deaths, up to 4,700 heart attacks, and up to 130,000 asthma attacks each year.
There are substantial and additional non-monetized benefits associated with reduced exposure to mercury and other harmful pollutants regulated by the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards.
Moreover, in spite of the power industry’s claims, reducing these emissions has proven much less expensive than initially projected. Major power companies such as AEP, NRG, and FirstEnergy have been reporting to their investors that the costs of the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards are as much as 70 percent lower than they first estimated.
The bottom line is that the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards are an extraordinarily beneficial public health measure and are providing healthier, longer lives for millions of Americans at a fraction of the costs predicted.
Second — the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards can and should continue to be implemented while EPA amends its “appropriate and necessary finding.”
The Supreme Court’s opinion did not prohibit the implementation of the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards – and in the past, the appellate courts have often allowed Clean Air Act regulations to remain in place while EPA amends them to address technical or legal issues.
In this case, a large majority of American power plants are already in compliance with the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards — in many instances because they have been upgrading pollution controls to comply with state emission standards or other Clean Air Act requirements. M.J. Bradley & Associates recently estimated that about 70 percent of the U.S. coal fleet had installed pollution controls to comply with the standards by the April 2015 deadline. In addition, a substantial number of plants have received one-year extensions to this compliance deadline and are now working to install pollution controls by April 2016.
Given the importance of the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards to public health, and the overwhelming likelihood that EPA will be able to quickly address the Court’s decision, there is no reason that power plants should be allowed to delay installing pollution controls or cease operating already-installed pollution controls.
Third – the Supreme Court decision has no adverse implications for EPA’s Clean Power Plan – despite the wild claims being made by some opponents of these vital limits on carbon pollution from power plants.
The Mercury and Air Toxics Standards and the Clean Power Plan are based on entirely separate Clean Air Act authorities that reside in separate parts of the statute. The authority EPA is acting on to develop the Clean Power Plan expressly provides for the consideration of costs, and EPA has carefully taken costs into account in the Clean Power Plan in the manner required by the statute. Thus, claims that the ruling on the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards should somehow cast doubt on the legality of the Clean Power Plan are severely misguided.
Summing It Up
Marian Burton, president of the American Academy of Pediatrics, summed it up perfectly back in 2011, when the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards were first proposed:
Dirty air makes children sick … If you think it’s an expensive process to put a scrubber on a smokestack, you should see how much it costs over a lifetime to treat a child with a preventable birth defect.
That’s why hundreds of thousands of Americans sent comments to EPA in support of the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards.
It’s why EDF and so many other health, environmental, and social justice groups will go back to the D.C. Circuit Court to defend the standards.
We’ll keep fighting to make sure the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards are fully implemented so we can realize the promise of the Clean Air Act — and make sure all Americans have safe, healthy air to breathe.