Just Two Actions May Stop the Planet’s Runaway Warming
 I was 15 and I was trying to impress a boyfriend with my rollerblading skills — from the top of a steep hill. Before I knew it, I was flying uncontrollably toward traffic. I knew I needed to both slow down and change course . . . or things wouldn’t end well.
I was 15 and I was trying to impress a boyfriend with my rollerblading skills — from the top of a steep hill. Before I knew it, I was flying uncontrollably toward traffic. I knew I needed to both slow down and change course . . . or things wouldn’t end well.
I did, and I survived, but I’ve recently thought about that day and those actions as I have considered the urgency needed for the planet to slow down and change course as the climate warms. With two major actions, we can slow the rate of global warming while also preventing “runaway” warming: nations must reduce emissions of both short-lived and long-lived pollutants.
All emissions are not equal
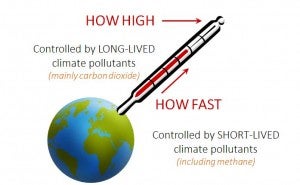
The way people talk and think about the long and short-term impacts of various greenhouse gasses is critical for making smart policy decisions that can effectively slow how fast the climate changes while limiting warming in the future.
While the maximum extent of warming relies on carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions because they last for centuries in the atmosphere, the rate of climate change is controlled by short-lived climate pollutants, such as methane.
Like carbon dioxide, methane is a gas that warms the Earth by trapping heat. Pound for pound, methane is more than 100 times more powerful than CO2 because methane is much more efficient at absorbing heat. But that number changes depending on how far out you look.
Comparing emissions of gases with vastly different radiative impacts and atmospheric lifetimes requires a metric that depends on what timeframe you care about, such as the next decade or next century. One way scientists deal with the temporal differences is by measuring the global warming potential of gases over two time periods: 20 years and 100 years.
Methane is 84 times more effective at trapping heat than CO2 over the first 20 years after they are both emitted, and 28 times more effective over 100 years, because most of the methane breaks down in the first 50 years after it is released due to oxidizing chemical reactions. When discussing what actions to take to reduce methane we must think about methane’s potency in both timeframes.
Our best chance of combating climate change
Since the Industrial Revolution, methane in the atmosphere has increased by a whopping 150 percent. While in the same period, CO2 levels have gone up 40 percent. Around one quarter of today’s human-caused warming is attributable to emissions of methane, while human-caused CO2 emissions account for around half.
The administration of U.S. President Barack Obama is currently undertaking efforts to reduce emissions of some of the most damaging greenhouse gas emissions responsible for climate change: methane pollution from oil and gas operations and carbon dioxide from coal-fired power plants. This strategy has prompted questions about which climate pollutant should take priority. But the discussion of whether to cut methane emissions first and carbon dioxide later — or vice versa — is not helpful or necessary. We need a two-pronged strategy to stay safe.
Understanding the urgent need to reduce all types of climate pollution, the Obama administration is expected to move forward with rules to mitigate both methane and carbon dioxide in the next few months. This summer the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is expected to propose the first ever direct regulation of methane emissions from new and modified sources in the oil and gas industry, and finalize its Clean Power Plan to reduce carbon dioxide from coal-fired power plants.
Another agency, the U.S. Bureau of Land Management, is also expected to soon propose important rules to reduce wasteful venting, flaring and leaking of methane associated with the production of oil and natural gas on public lands.
Nations cannot solve the climate crisis and prevent serious impacts without simultaneously reducing both short-lived and long-lived climate pollutants. Reducing CO2 will limit the overall warming the planet will experience generations from now, which will have profound impacts on limiting sea level rise and other dangerous consequences.
Reducing warming caused by methane during our lifetime will also reduce the likelihood of extreme weather events and species extinctions — and, a slower rate also provides more time for societies and ecosystems to adapt to changes.
This post originally appeared on LiveScience.












