Tom Neltner, Senior Director, Safer Chemicals Initiative and Roya Alkafaji, Manager, Healthy Communities
What Happened: The State of New Jersey published an interactive map showing potential sources of lead exposure for any given address in the state. Currently, the map specifically looks at lead-based paint in housing, though the State has plans to expand this to include other sources of lead, including drinking water from lead service lines (LSLs).
Why It Matters: The availability of address-specific information is important to engage residents, potential home buyers, and renters so they can make better informed decisions about protecting their families from harmful lead exposure. New Jersey is the first state to move beyond neighborhood-level mapping of lead risks to provide specific information about lead at the address level.
The map uses housing age as an indicator to assess risk to lead exposure, which is an excellent place to start because it is relevant to the prevalence of both lead-based paint and lead in drinking water.
As more information is added on lead pipes, lead-contaminated soil, and nearby commercial operations that release lead, as well as details on lead poisoning prevention requirements, the map will become a critical tool in the effort to comprehensively consider lead risks and drive exposure closer to zero.
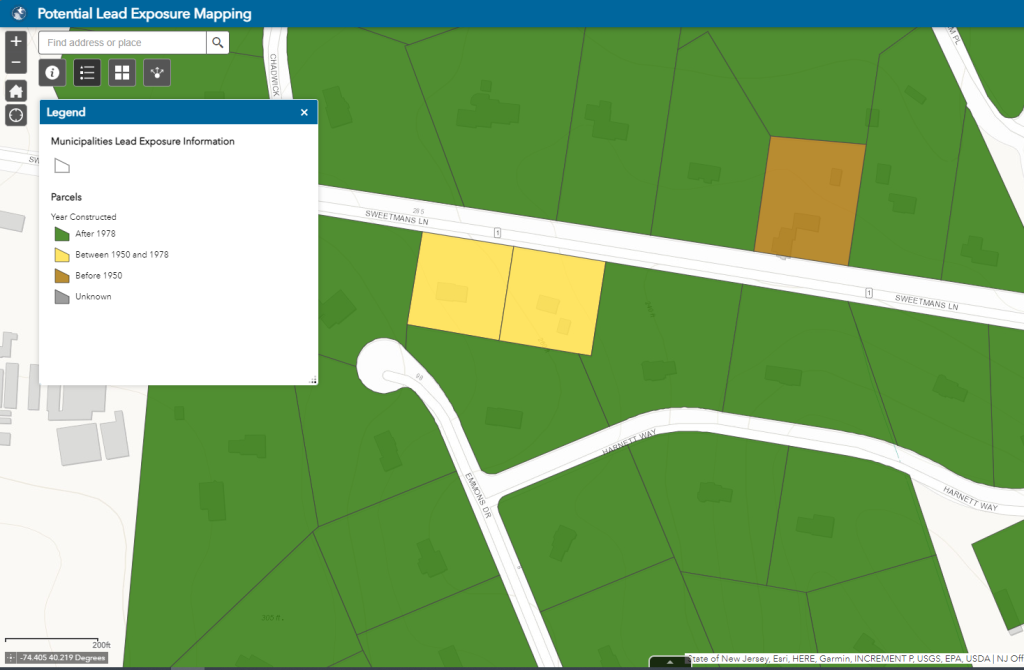
Source: New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection Potential Lead Exposure Mapping (click on Lead-based paint tab at the top and zoom in until you see parcel-level detail with color overlays)









