What’s new: A new report has found the cancer-linked endocrine disruptor, nonylphenol (NP), in one-third of tested Indian clothing products at levels exceeding European Union (EU) safety standards.
Scientists also detected NP in major Indian rivers downstream from textile hubs at levels that significantly exceeded international water quality standards. The report, Toxic Threads, was published by the Indian environmental research and advocacy organization Toxics Link in partnership with Environmental Defense Fund.

Common industrial applications of nonylphenol chemical (Toxics Link)
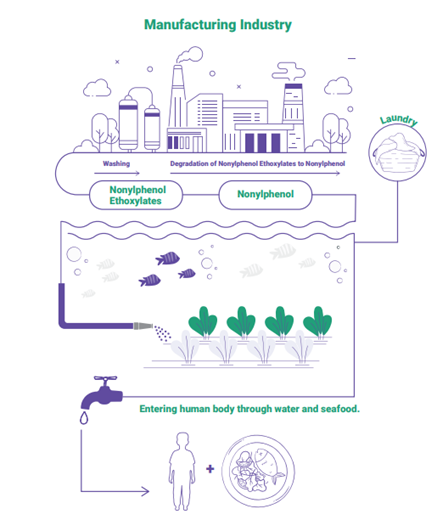
What is NP and where does it come from? NP is a chemical byproduct of degrading nonylphenol ethoxylates (NPEs), which manufacturers across several sectors use as a base ingredient in detergents, wetting agents, dispersants, defoamers, de-inkers and antistatic agents. Textile producers use NPEs most commonly in cleaning agents.
The Toxic Threads report’s key findings include:
- NP was detected in 15 of the 40 products examined (about 35%).
- NP levels in 13 out of the 40 products exceeded the current EU limit (<100 mg/kg).
- 60% (9 out of 15) of baby and children’s products contained NP.
- Female innerwear made with hosiery had the highest NP concentration of all garment types.
- Significant NP contamination was found in several rivers near key Indian textile hubs.
- NP’s presence in downstream locations and absence upstream strongly suggests point-source pollution from industrial activities, particularly textile manufacturing.
Why it matters: NP is an endocrine disruptor and has been linked to cancer. People, particularly children, can be exposed to it through everyday products they touch or might put in their mouths. NP’s persistence (how long it lasts), toxicity and ability to build up in the body over time makes it a significant threat to human health, the environment, marine ecosystems and the food chain. Because many textiles produced in India are exported, the associated health risks could extend to consumers in importing countries that don’t regulate NP in clothing, such as the United States.
How can India protect its people and aquatic life from the dangers of NP? While several countries have taken proactive measures, India has yet to fully regulate against the harms of NP and NPE contamination.
The report recommends Indian leaders take decisive action to align with global efforts in restricting NP and NPE use. Strengthening regulations and promoting safer alternatives in textile manufacturing and consumer products are key to safeguarding human and environmental health and ensuring sustainable market practices.
Go deeper: Read the full Toxic Threads report here.