NOTE: This is the second of a series about EPA’s prioritization of existing chemicals.
What Happened?
EPA just proposed to designate five chemicals, including the widely-known toxic chemical vinyl chloride, as high-priority chemicals – meaning they are toxic to human and/or environmental health. If finalized, these chemicals will immediately undergo the risk evaluation process under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA).
When designating these chemicals as high priority and moving forward in assessing their health risks, EPA can – and should – consider exposures to multiple chemicals that can cause the same health harms. To demonstrate the importance of these cumulative exposures, we conducted analysis on co-exposures to these five chemicals and submitted this analysis to EPA for greater consideration of real-world risks faced by individuals exposed to these toxic chemicals.
Why It Matters
Communities near industrial facilities are often exposed to multiple chemicals that cause the same health effects. Evaluating the health risk of these chemicals individually, as currently done by EPA’s TSCA program, often underestimates the true risks communities face. Additionally, many of these fenceline communities experience a variety of non-chemical stressors that exacerbate health effects from chemical exposure, such as physiological stress from poverty and racial discrimination, limited access to healthcare, or health effects from climate stressors like flooding and heat. Failing to consider these cumulative stressors on health in chemical risk evaluations often underestimates the actual risks these chemicals can pose to human health.
Our Take
Our analysis of Toxics Release Inventory (TRI) data from 2016-2021 shows that many chemicals that cause the same health effects – such as cancer, central nervous system (neurological), cardiorespiratory, liver, kidney, and thyroid, and reproductive and developmental effects – are often released together from the same facilities. For example, chemicals that cause cardiorespiratory effects are released with at least one other chemical that causes these same effects 74% of the time.
For the five chemicals that have just been proposed as high priority under TSCA, all are known or probable carcinogens with some causing other adverse health effects. Based on our analysis, there are a few notable co-releases that EPA should consider when assessing cumulative risk with other chemicals causing the same harms. For example, creosotes, which are also probable carcinogens that can cause liver, kidney, and thyroid effects, are released 11% of the time with acrylonitrile, 18% with aniline, 11% with vinyl chloride, and 11% with 4,4-methylene bis(2-chloroaniline).
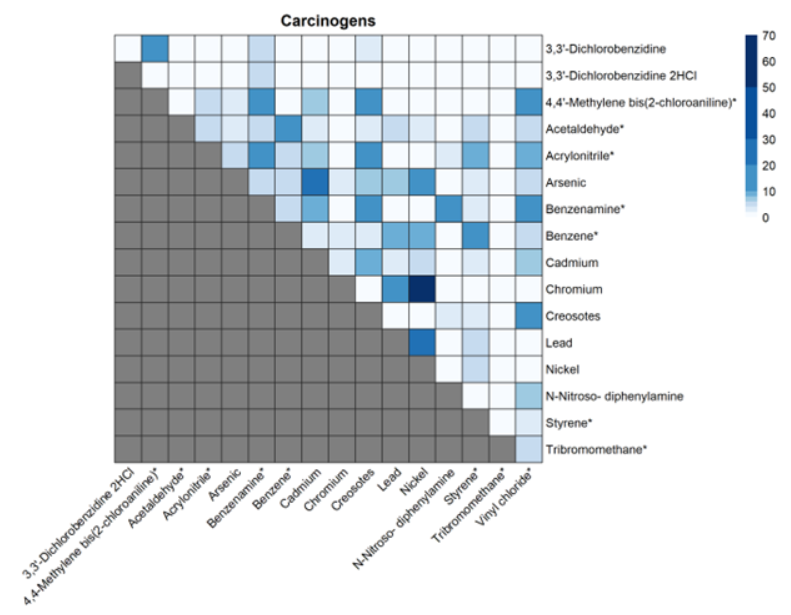
Heatmap of co-releases of carcinogenic chemicals that are part of the TSCA Workplan. Legend represents the percentage of facilities releasing both chemicals out of the facilities releasing at least one of the pair of chemicals. Stars represent the 15 chemicals that were considered as part of TSCA’s pre-prioritization.
To demonstrate that EPA should also consider non-chemical stressors such as climate and environmental justice in its TSCA prioritization and risk evaluations, we looked at the vulnerability of communities to climate and environmental justice factors in areas where certain chemicals are released using EDF’s Climate Vulnerability Index. On average, vinyl chloride is released into communities with higher vulnerability than other chemicals analyzed – up to 12% higher than the average for other carcinogenic chemicals.
What’s Next?
EPA is now accepting comments on their proposal to designate these five chemicals as high priority, and we plan to submit comments to support the high priority designation. If finalized, EPA will begin risk evaluations for these chemicals. We hope EPA will consider cumulative risk and environmental justice as it moves through this process.
In our next post in this series, we will recommend ways EPA can improve its prioritization process by considering risks from transportation and distribution of chemicals.