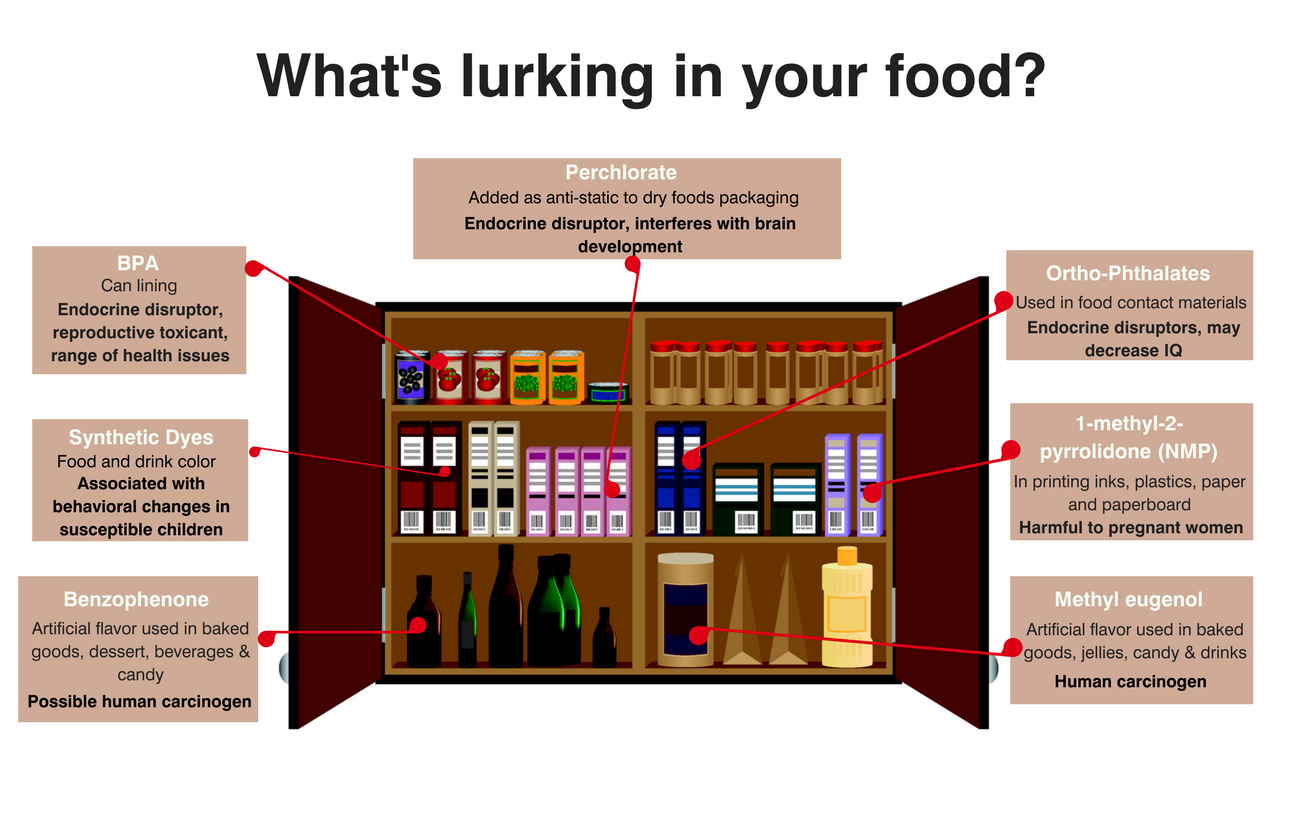
Today, Environmental Defense Fund joined other groups in challenging a Food and Drug Administration (FDA) rule that allows chemical and food manufacturers to decide for themselves – in secret – what chemicals and food additives can be added to foods. The practice puts our health at risk and does not fulfill Congress’ requirement that FDA determine that chemical additives are safe before they can be used in food.
Americans would be shocked to learn that food companies routinely add novel chemicals to our food without first getting FDA approval. In doing so, the companies are exploiting a loophole exempting ingredients “Generally Recognized as Safe” (GRAS) from formal FDA review and approval.
Originally intended for ingredients like vinegar and olive oil, industry now abuses the GRAS loophole by bypassing FDA review and making safety determinations in secret. The alarming result: even FDA does not know what is in our food. In fact, FDA has no way to know what chemicals are actually being used in which food or in what quantities—even in baby food.
Last year, the FDA issued a final rule formalizing this outrageous practice. We described this decision as a lost opportunity for safer food additives when the decision was made. Today, EDF and our colleagues at the Center for Food Safety (CFS), Breast Cancer Prevention Partners, Center for Science in the Public Interest, and Environmental Working Group, represented by CFS and the environmental law firm Earthjustice, joined in filing suit against the FDA for unconstitutionally and illegally delegating that authority to self-interested food and chemical manufacturers.
It is disappointing that the groups were forced to take legal action. In addition to being a bad policy that doesn’t comply with law, or protect public health, the FDA is oddly out of touch with public sentiment. Just last week an industry funded survey showed overwhelming consumer concern about chemicals in food, including cancer causing chemicals, while showing diminished confidence in the food supply. This continues a trend that has been building for years. Food companies would be wise to take notice: adding secret chemicals without FDA scientific review to our food is no way to improve confidence in their products.
But with thousands of secret chemicals in our food, we can’t wait for industry or FDA to wise up. Today’s lawsuit seeks to force FDA to do what should be common sense—determine that food additives are safe before they can be added to our food.