 Aliso Canyon was a big methane release, especially in Los Angeles, but in the grand scheme of methane released every day by the nation’s oil and gas industry, it was a blip. And recent footage from Texas, coupled with a new study of over 8,000 oil and gas wells gives a glimpse at the kind of leaks that are happening outside of California’s borders – leaks that have huge implications for the state.
Aliso Canyon was a big methane release, especially in Los Angeles, but in the grand scheme of methane released every day by the nation’s oil and gas industry, it was a blip. And recent footage from Texas, coupled with a new study of over 8,000 oil and gas wells gives a glimpse at the kind of leaks that are happening outside of California’s borders – leaks that have huge implications for the state.
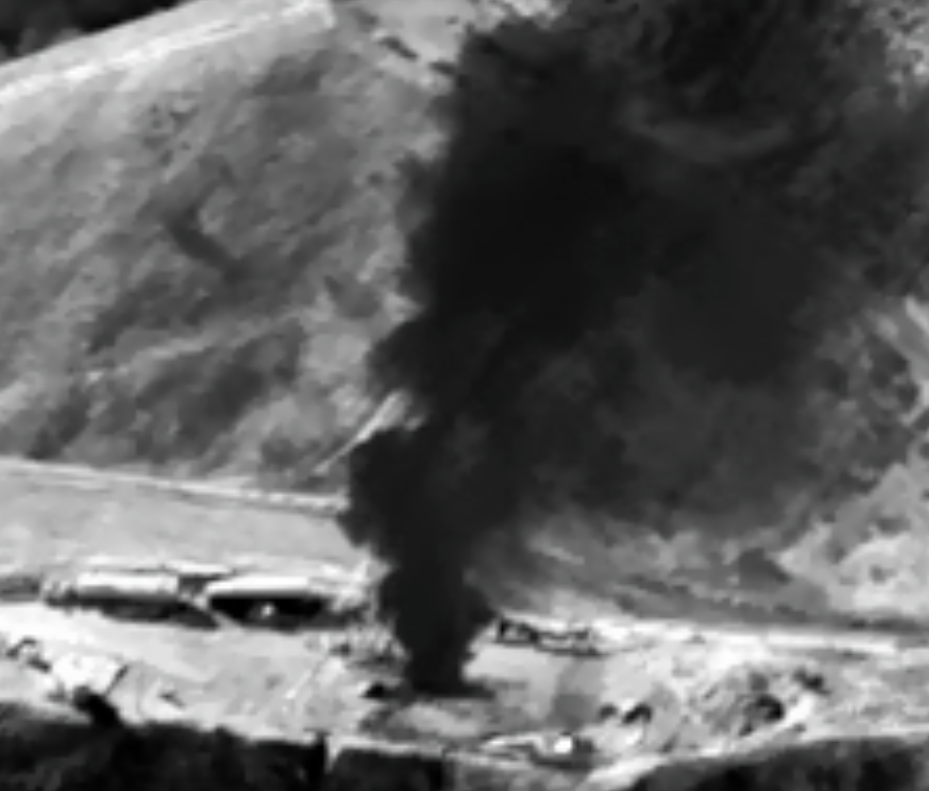
The Texas infrared footage shows a cloud of methane leaking from a pump jack in an oil field in Texas’ Permian Basin. While these smaller leaks may not be as egregious as the one at Aliso Canyon, they often go undetected and unaddressed, adding up to a large amount of pollution. And as these leaks happen in Texas – with little plans to stop them – the climate footprint of the gas supply system continues to increase.
So what does this have to do with California? California imports nearly 90 percent of its natural gas from regions across western North America, with a large portion coming from Texas production areas like the Permian and Anadarko basins. To put it another way: when it comes to the climate, what happens in Texas doesn’t stay in Texas. So even while progress is happening to cut oil and gas pollution in the Golden State, there is still a lot of work to be done to make sure imported gas isn’t responsible for significant climate damage before it gets here. Read More
 The leak in Southern California Gas Company’s Aliso Canyon Facility released a massive amount of methane – a powerful climate change pollutant. Like other catastrophes, now that the pollution release is stemmed, the focus shifts towards cleanup and mitigation (as well as establishing causation, preventing recurrence, and pursuing legal actions).
The leak in Southern California Gas Company’s Aliso Canyon Facility released a massive amount of methane – a powerful climate change pollutant. Like other catastrophes, now that the pollution release is stemmed, the focus shifts towards cleanup and mitigation (as well as establishing causation, preventing recurrence, and pursuing legal actions). Methane leaking from pipes before natural gas is delivered to customers can have a large, harmful impact on the climate. This idea was first brought to light in a major
Methane leaking from pipes before natural gas is delivered to customers can have a large, harmful impact on the climate. This idea was first brought to light in a major 

