Key Findings and Recommendations
- Air pollution results in a large burden of childhood asthma across the country, and this burden is disproportionately borne by people of color.
- More than $100 million in grants from the Environmental Protection Agency is available for environmental justice initiatives, but targeting programs to alleviate the health impacts of air pollution to overburdened communities requires local-level health information that is often not readily available.
- We recommend health advocates and researchers work with local and state public health departments and impacted communities to access existing fine-scale data where available.
In the past, the lack of neighborhood-scale data on baseline disease rates, pollutant concentrations and children’s asthma has made it difficult to determine which U.S. communities bear the highest health burden from air pollution. Disparities in pollution exposures have been routinely underestimated. Generating more fine-scale data, together with advances in hyperlocal air monitoring, will make visible the disparities in exposure to air pollution across and within neighborhoods, allowing us to target mitigation and prevention efforts for maximum benefit.
We now have an opportunity to make significant progress towards identifying, prioritizing and addressing the harms faced by the most burdened communities. EPA has made available over $100 million dollars for grants to advance environmental justice, including health impact assessments. Grant recipients can use the funds to obtain health information at the neighborhood level, data essential for identifying communities with the highest burden of air pollution health impacts. The application deadline is April 14, 2023.
Pollution and racism
Using new air monitoring techniques, advances in modeling, and community-based participatory research, studies confirm that neighborhoods which have experienced historical racism also experience higher levels of air pollution.
Decades of discriminatory and racist policies, practices and disenfranchisement have resulted in the disproportionate exposure to pollution sources in communities of color, along with disinvestment in housing and economic opportunities in these communities. Communities of color and areas of low wealth therefore face exposure to higher levels of air pollution and are more vulnerable to that air pollution, resulting in heavier health burdens borne by families.
Air pollution data is only half of the story
While air pollutant exposure is important in determining the effect of that pollutant on the health of a community, social factors and existing disease burden and risk play a large role in the impact that pollutant will have on the total health burden attributable to a pollutant in a community.
Existing disease burdens and risks in populations are reflected in “baseline disease rates,” a key public health metric documented by public health agencies. Baseline disease rates vary within cities, but those rates are rarely made publicly available for use in risk assessment.
Gaps in baseline disease data availability limit the ability of health impact assessments to determine which communities have existing vulnerabilities to the harmful effects of air pollution. For example, while studies of pediatric asthma attributable to nitrogen dioxide, a traffic-related air pollutant, have estimated there are 200,000 affected children living in American cities, these studies have relied on national-level estimates of asthma incidence. These national-level estimates hinder the ability of researchers to determine which areas within cities are experiencing the highest burden of asthma attributable to asthma.
Local-level health data is needed to identify risks to overburdened communities
The public health information available from city to city and within cities is a mix of fine-scale data (ZIP code level) and coarse-scale data (ZIP3 – aggregated data based on ZIP code information, roughly the size of counties.) The assessment of health risks, factors and outcomes can vary greatly depending on which level of data is used.
Studies have repeatedly shown that using fine-scale baseline disease rates can make a profound difference when mapping the spatial distribution of health burdens attributable to air pollutants and on the ability to quantify disproportionate impacts in disadvantaged populations. For example, in an analysis of within-city air pollution risks in the San Francisco Bay Area of California, we found the highest census block group baseline mortality rate was 12 times higher than the rates in the census block group with the lowest rates, while the highest county rate was only four times greater than the lowest county mortality rate.
Lack of fine scale data leads to unreliable analysis
Our work in New Jersey highlights the pitfalls of using only coarsely-resolved spatial data in identifying those communities that are at highest risk of the health burdens of air pollution. An analysis of the impact of pollution in that state found that 18,000 asthma emergency room visits by children could be attributed to fine particle pollution and 70% of those impacts were among communities of color (Asian, Black and Native American) and Hispanic populations.
Comparing the results using coarse-scale and fine-scale data, we found that:
- Analysis using coarse-resolution emergency room visit information overestimated the burden to white populations. It underestimated the burden to people of color by as much as 90%.
- Using fine-scale data, we found emergency room visits for the ZIP code with the highest burden to be 1.5 times higher than the highest burden estimated using coarse-resolution data.
- We also found that using fine-scale data revealed double the variation between the ZIP code with the highest risk of PM-attributable visits and ZIP codes with the least risk of PM-attributable visits. Variation allows us to observe the relative disparities in risk within a community that are not otherwise observable with coarse-scale baseline disease data.
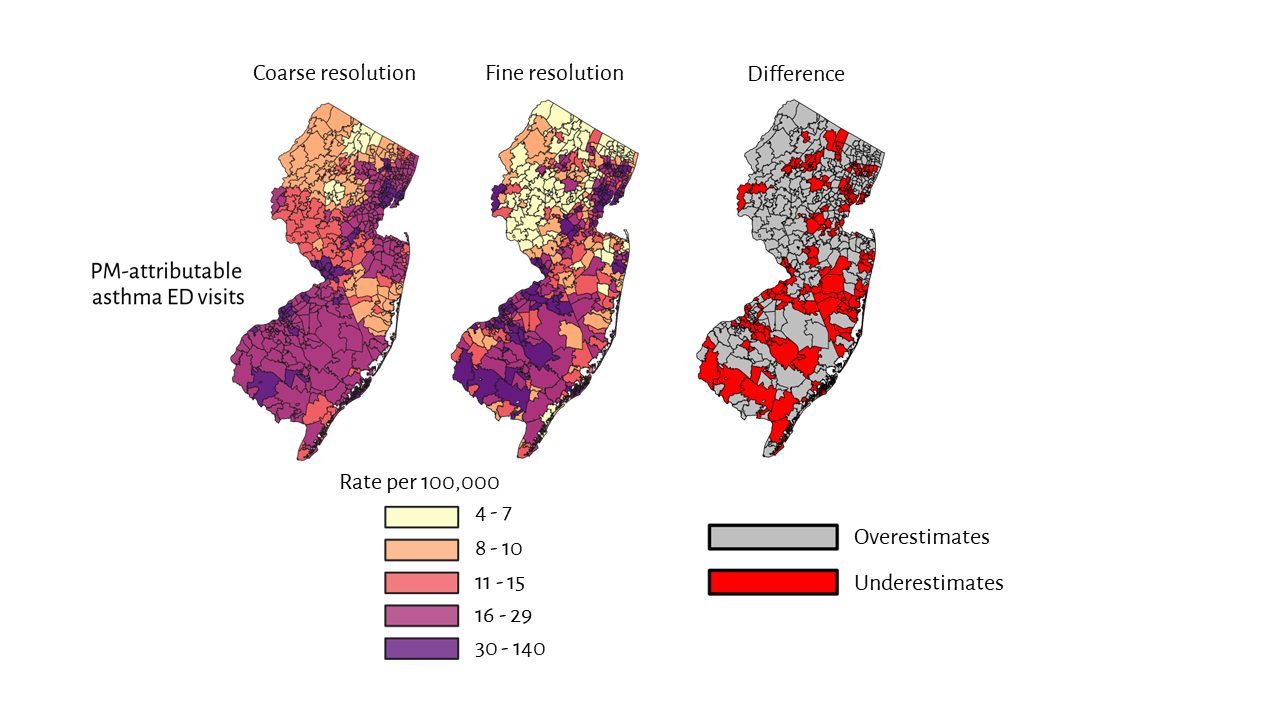
The use of coarse-resolution (ZIP3) asthma emergency department visit data may underestimate PM-attributable asthma burdens (number of cases per 10,000) among non-white populations when compared to fine-scale (ZIP) data. Red shows communities where coarse-resolution health data underestimates risks.
Local-level health information can help EPA and other funders to identify and direct resources to the communities that need it most, which are too often communities of color facing legacy injustices.
Our work in the Bay Area of California highlights the need for fine-resolution data on baseline disease rates, as pollutant concentrations alone were unable to capture the variation of air pollution health risks within Oakland.
The maps shown in Figure 2 are of the neighborhoods of West Oakland. Looking only at the spatial distribution of the highest pollutant concentrations (A), the area of highest risk appears to be the truck traffic corridor of I-880. However, when we incorporated census block group baseline disease rates (B), provided by the Alameda County Public Health Department, we found that the area of highest risk, and therefore where the largest emission reductions could result in the largest reduction in health burden, was another area of West Oakland where both baseline mortality rates and pollution levels were elevated.
Pollutant concentrations and county baseline disease rates alone would not have revealed this vulnerable neighborhood. A better understanding of pollution hotspots can help direct federal funds intended to address long legacies of pollution burdens to communities where they’re most needed.
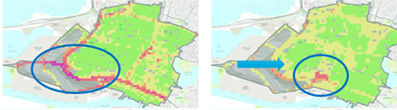
West and Downtown Oakland. The map on the left (A) shows the spatial distribution of pollutant concentrations, with high concentrations highlighted in the blue circle near major roadways. The map on the right (B) shows the spatial distribution of air pollutant attributable health burdens when the spatial distribution of underlying disease patterns are taken into consideration. The area of highest air pollutant attributable health burdens in map (B) is highlighted in the blue circle.
Ways to expand and improve local-level health data
Past investment in satellite-derived estimates and local air pollution monitoring has resulted in making exposure disparities visible. Similar investment is required now for developing fine-scale data on baseline disease rates, which will enable identification of communities with the highest air pollution-attributable health burdens.
Mechanisms currently exist for developing more fine-resolution data on baseline asthma emergency department visits. As part of the analysis in New Jersey described above, we purchased discharge-level emergency department visit data for New Jersey from 2016 to 2019 from the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project’s State Emergency Department Database (HCUP SEDD). We urge the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, which manages the HCUP SEDD, to develop baseline asthma emergency department visit datasets and that the Agency update these datasets annually and make them publicly available.
We recommend that health advocates and researchers work with local and state public health departments to access existing fine-scale data where available. We have found that local health departments often have the data needed but lack the resources to dedicate staff and expertise to process and analyze the information. As an example, EDF has had success working with the Alameda County Public Health Department to develop mortality rates at the census block group level. Other impediments to developing baseline disease rates include lack of funding and concerns about privacy.
Deadlines approaching for funding opportunities to develop local-level health data
EPA is accepting environmental justice grant applications through April 14, 2023 through two avenues: the EJ Collaborative Problem-Solving Cooperative Agreement Program (EJCPS) and the Environmental Justice Government-to-Government (EJG2G) program.
While both grant programs are relevant to the use of local-level health data, the Government-to-Government grants allow community-based organizations to partner with their local health department on use of local-level data in health impact assessments. This can help alleviate the problem discussed above regarding inadequate staffing and expertise at local health departments.
Of the five broad categories listed in the funding announcement, use of local-level health data fits under the category “community-led air and other pollution monitoring, prevention, and remediation, and investments in low- and zero-emission and resilient technologies and related infrastructure and workforce development that help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and other air pollutants.”













