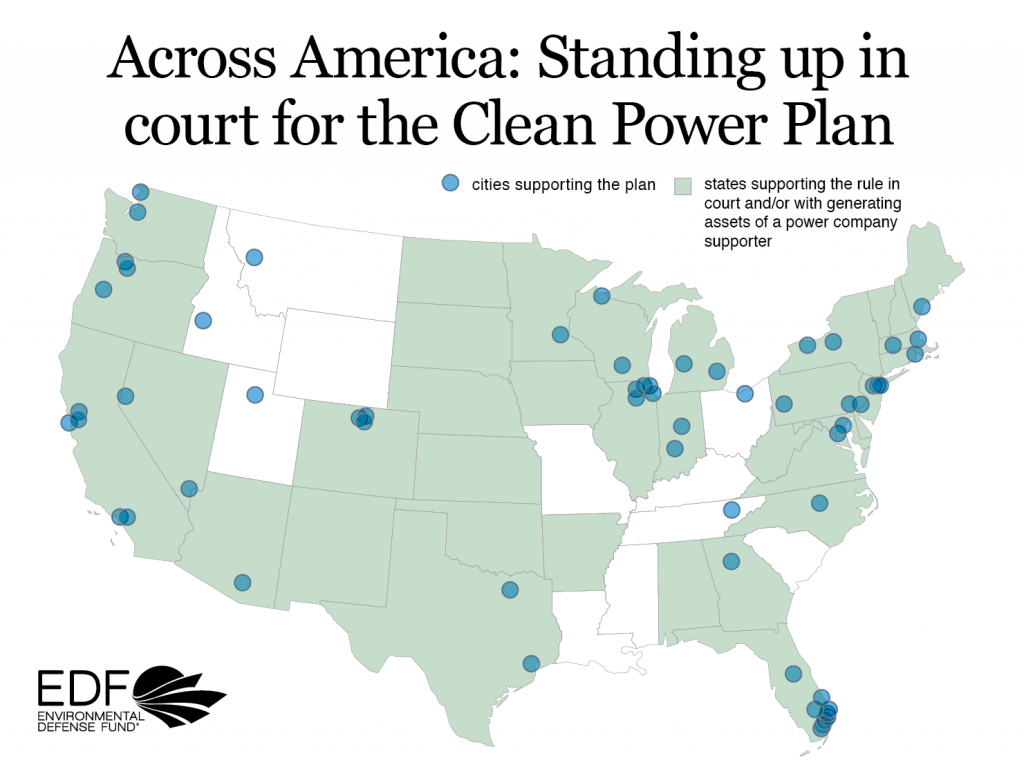
Just hours after President Trump signed an executive order to weaken a wide range of America’s important climate and heath protections, the Administration filed a motion to delay the D.C Circuit court’s review of the Clean Power Plan case.
That’s only the first of what we expect will be many attacks on the Clean Power Plan – our only nationwide limit on climate pollution from power plants. However, the Clean Power Plan is popular with Americans across the country, and an extraordinarily broad and diverse group of leaders and experts from across America have announced their support for the Clean Power Plan since the executive order.
You’ll likely be hearing a lot about this story in the near future. While you follow the news, here are 10 things you should know about the Clean Power Plan.
1. The Clean Power Plan is expected to save thousands of lives and protect the health of Americans across the country. According to EPA’s analysis, when fully implemented the Clean Power Plan will:
- Prevent up to 3,600 premature deaths each year
- Prevent up to 1,700 heart attacks each year
- Prevent up to 90,000 asthma attacks each year
- Prevent up to 300,000 missed work days and school days each year
2. The Clean Power Plan’s pollution reduction targets are eminently achievable.
Carbon pollution from the power sector has decreased by more than 20 percent since 2005, meaning that we’re already more than two-thirds of the way toward meeting the Clean Power Plan standards for 2030. In fact, most states that are litigating against the Clean Power Plan are on track to meet these pollution limits. The Clean Power Plan is essential to ensure that this momentum is sustained and that power sector investments in clean energy are deployed in a way that maximizes their pollution reduction benefits.
3. The Clean Power Plan can reduce electricity bills for families.
The Clean Power Plan gives states and power companies tremendous flexibility in deciding how to meet the pollution reduction targets – including through cost-effective energy efficiency measures that save families money. Independent analyses of the Clean Power Plan have found that average bills could decline by as much as 11 percent as a result of these measures. That’s why leading consumer and ratepayer advocates, including Consumers Union, support the Clean Power Plan.
4. Our vibrant clean energy sector employs millions of Americans and it is thriving.
According to a recent assessment by Advanced Energy Economy, the United States clean energy sector is now a rapidly-growing, $200 billion industry that employs 3.3 million Americans.
5. Clean energy is creating economic opportunities in communities across the nation.
The American Wind Energy Association estimates that 70 percent of wind farms are located in low-income counties, and that wind developers currently pay $222 million a year in lease payments to U.S. farmers, ranchers and other rural landowners. AWEA also estimates that wind energy has created more than 25,000 manufacturing jobs in 43 states.
6. The Administration’s promises that revoking climate and clean air protections will bring back coal jobs are false, as the coal industry itself recognizes.
Independent analyses have found that employment in the coal industry has been falling steadily since 1975, due largely to changing methods of coal production and – in more recent years – by competition from inexpensive natural gas. These trends cannot be reversed by revoking the Clean Power Plan or other protections for clean air and clean water. Even coal company executives have acknowledged that the executive order can’t bring mining jobs back.
7. An extraordinarily broad and diverse coalition is supporting the Clean Power Plan in court.
This coalition includes, among others: eighteen states and sixty municipalities; power companies that own and operate nearly ten percent of the nation’s generating capacity; leading businesses like Amazon, Apple, Google, Mars, and IKEA; former Republican heads of EPA; public health and environmental organizations; consumer and ratepayer advocates; faith organizations; and many others.
8. Large majorities of Americans in red and blue states alike support reducing climate pollution from existing power plants.
According to a recent national poll, 69 percent of Americans support placing limits on climate pollution from existing power plants – including a majority of Americans in every Congressional district in the country.
9. The nation’s leading businesses support policies to reduce climate pollution.
Just this month, over 1,000 companies and investors called on the Trump Administration to continue low-carbon policies, noting that “failure to build a low-carbon economy puts American prosperity at risk” and that “the right action now will create jobs and boost U.S. competitiveness.”
10. The Clean Power Plan rests on a rock-solid legal foundation.
The Supreme Court has held on three separate occasions that Congress has vested EPA with the responsibility – and the tools – to reduce carbon pollution under the Clean Air Act. Numerous legal experts – including drafters of the Clean Air Act, former EPA Administrators who served under Presidents Nixon, Reagan, and Bush, and former state energy and environmental officials – have affirmed the strong legal basis for the Clean Power Plan
Attacks on the Clean Power Plan and our other clean air protections present an unprecedented attack on our children’s health. It takes our nation backwards – to more pollution, more disease – even though Americans support forward progress towards clean air and clean energy.

 This week has brought alarming indications that the Trump Administration is poised to roll back life-saving, common-sense climate protections with no plan for replacing them — and that the head of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) rejects basic facts about climate change and the clean air laws he is charged with carrying out.
This week has brought alarming indications that the Trump Administration is poised to roll back life-saving, common-sense climate protections with no plan for replacing them — and that the head of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) rejects basic facts about climate change and the clean air laws he is charged with carrying out.